A mechanism of suppression of TGF-beta/SMAD signaling by NF-kappa B/RelA
- PMID: 10652273
- PMCID: PMC316349
A mechanism of suppression of TGF-beta/SMAD signaling by NF-kappa B/RelA
Abstract
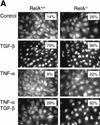
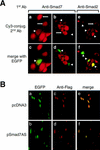
A number of pathogenic and proinflammatory stimuli, and the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) exert opposing activities in cellular and immune responses. Here we show that the RelA subunit of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB/RelA) is necessary for the inhibition of TGF-beta-induced phosphorylation, nuclear translocation, and DNA binding of SMAD signaling complexes by tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). The antagonism is mediated through up-regulation of Smad7 synthesis and induction of stable associations between ligand-activated TGF-beta receptors and inhibitory Smad7. Down-regulation of endogenous Smad7 by expression of antisense mRNA releases TGF-beta/SMAD-induced transcriptional responses from suppression by cytokine-activated NF-kappaB/RelA. Following stimulation with bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), or the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta, NF-kappaB/RelA induces Smad7 synthesis through activation of Smad7 gene transcription. These results suggest a mechanism of suppression of TGF-beta/SMAD signaling by opposing stimuli mediated through the activation of inhibitory Smad7 by NF-kappaB/RelA.
Figures




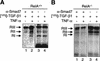
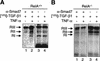

References
-
- Arsura M, Wu M, Sonenshein GE. TGF beta 1 inhibits NF-kappa B/Rel activity inducing apoptosis of B cells: Transcriptional activation of I kappa B alpha. Immunity. 1996;5:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Arsura M, FitzGerald MJ, Fausto N, Sonenshein GE. Nuclear factor-kappaB/Rel blocks transforming growth factor beta1-induced apoptosis of murine hepatocyte cell lines. Cell Growth Differ. 1997;8:1049–1059. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AS., Jr The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:649–683. - PubMed
-
- Ballermann BJ, Dardik A, Eng E, Liu A. Shear stress and the endothelium. Kidney Int Suppl. 1998;67:S100–S108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
