Dynamic organization of chromosomal DNA in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 10652275
- PMCID: PMC316355
Dynamic organization of chromosomal DNA in Escherichia coli
Abstract
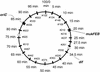
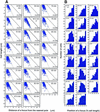
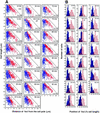
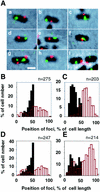
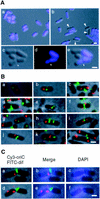
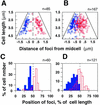
We have revealed the subcellular localization of different DNA segments that are located at approximately 230-kb intervals on the Escherichia coli chromosome using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). The series of chromosome segments is localized within the cell in the same order as the chromosome map. The large chromosome region including oriC shows similar localization patterns, which we call the Ori domain. In addition, the localization pattern of the large segment including dif is characteristic of the replication terminus region. The segment also shows similar localization patterns, which we call the Ter domain. In newborn cells, Ori and Ter domains of the chromosome are differentially localized near opposite cell poles. Subsequently, in the B period, the Ori domain moves toward mid-cell before the initiation of replication, and the Ter domain tends to relocate at mid-cell. An inversion mutant, in which the Ter domain is located close to oriC, shows abnormal subcellular localization of ori and dif segments, resulting in frequent production of anucleate cells. These studies thus suggest that the E. coli chromosome is organized to form a compacted ring structure with the Ori and Ter domains; these domains participate in the cell cycle-dependent localization of the chromosome.
Figures
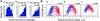
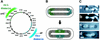
References
-
- Cornet F, Louarn J, Patte J, Louarn JM. Restriction of the activity of the recombination site dif to a small zone of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Genes & Dev. 1996;10:1152–1161. - PubMed
-
- Glaser P, Sharpe ME, Raether B, Perego M, Ohlsen K, Errington J. Dynamic, mitotic-like behavior of a bacterial protein required for accurate chromosome partitioning. Genes & Dev. 1997;9:1160–1168. - PubMed
-
- Gordon GS, Sitnikov D, Webb CD, Teleman A, Straight A, Losick R, Murray AW, Wright A. Chromosome and low copy plasmid segregation in E. coli: Visual evidence for distinct mechanisms. Cell. 1997;90:1113–1121. - PubMed
-
- Hill TM. Features of the chromosomal terminus region. In: Neidhardt FC, et al., editors. Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: Cellular and molecular biology. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology; 1996. pp. 1602–1614.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
