Naphthalene degradation and incorporation of naphthalene-derived carbon into biomass by the thermophile Bacillus thermoleovorans
- PMID: 10653712
- PMCID: PMC91857
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.2.518-523.2000
Naphthalene degradation and incorporation of naphthalene-derived carbon into biomass by the thermophile Bacillus thermoleovorans
Abstract
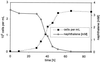
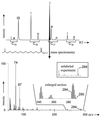
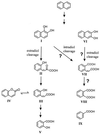
The thermophilic aerobic bacterium Bacillus thermoleovorans Hamburg 2 grows at 60 degrees C on naphthalene as the sole source of carbon and energy. In batch cultures, an effective substrate degradation was observed. The carbon balance, including naphthalene, metabolites, biomass, and CO(2), was determined by the application of [1-(13)C]naphthalene. The incorporation of naphthalene-derived carbon into the bulk biomass as well as into specified biomass fractions such as fatty acids and amino acids was confirmed by coupled gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and isotope analyses. Metabolites were characterized by GC-MS; the established structures allow tracing the degradation pathway under thermophilic conditions. Apart from typical metabolites of naphthalene degradation known from mesophiles, intermediates such as 2, 3-dihydroxynaphthalene, 2-carboxycinnamic acid, and phthalic and benzoic acid were identified for the pathway of this bacterium. These compounds indicate that naphthalene degradation by the thermophilic B. thermoleovorans differs from the known pathways found for mesophilic bacteria.
Figures


References
-
- Adams D, Ribbons D W. The metabolism of aromatic compounds by thermophilic bacilli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 1988;17:231–244.
-
- Alexander M. Biodegradation and bioremedation. San Diego, Calif: Academic Press, Inc.; 1994. p. 12.
-
- Buswell J A, Twomey D G. Utilization of phenol and cresols by Bacillus stearothermophilus, strain PH24. J Gen Microbiol. 1975;87:377–379. - PubMed
-
- Cerniglia C E, Hebert R L, Szaniszlo P J, Gibson D T. Fungal transformation of naphthalene. Arch Microbiol. 1978;117:135–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

