Serum-stimulated, rapamycin-sensitive phosphorylation sites in the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4GI
- PMID: 10654941
- PMCID: PMC305580
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.3.434
Serum-stimulated, rapamycin-sensitive phosphorylation sites in the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4GI
Abstract
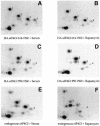
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) proteins play a critical role in the recruitment of the translational machinery to mRNA. The eIF4Gs are phosphoproteins. However, the location of the phosphorylation sites, how phosphorylation of these proteins is modulated and the identity of the intracellular signaling pathways regulating eIF4G phosphorylation have not been established. In this report, two-dimensional phosphopeptide mapping demonstrates that the phosphorylation state of specific eIF4GI residues is altered by serum and mitogens. Phosphopeptides resolved by this method were mapped to the C-terminal one-third of the protein. Mass spectrometry and mutational analyses identified the serum-stimulated phosphorylation sites in this region as serines 1108, 1148 and 1192. Phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors and rapamycin, an inhibitor of the kinase FRAP/mTOR (FKBP12-rapamycin-associated protein/mammalian target of rapamycin), prevent the serum-induced phosphorylation of these residues. Finally, the phosphorylation state of N-terminally truncated eIF4GI proteins acquires resistance to kinase inhibitor treatment. These data suggest that the kinases phosphorylating serines 1108, 1148 and 1192 are not directly downstream of PI3K and FRAP/mTOR, but that the accessibility of the C-terminus to kinases is modulated by this pathway(s).
Figures

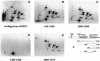


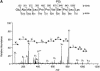

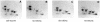
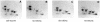
References
-
- Abraham R.T. (1998) Mammalian target of rapamycin—immunosuppressive drugs uncover a novel pathway of cytokine receptor signaling. Curr. Opin. Immunol., 10, 330–336. - PubMed
-
- Brown E.J. and Schreiber, S.L. (1996) A signaling pathway to translational control. Cell, 86, 517–520. - PubMed
-
- Browning K.S., Maia, D.M., Lax, S.R. and Ravel, J.M. (1987) Identification of a new protein synthesis initiation factor from wheat germ. J. Biol. Chem., 262, 538–541. - PubMed
-
- Chen C.A. and Okayama, H. (1988) Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques, 6, 632–638. - PubMed
-
- Craig A.W.B., Haghighat, A., Yu, A.T.K. and Sonenberg, N. (1998) Interaction of polyadenylate-binding protein with the eIF4G homologue PAIP enhances translation. Nature, 392, 520–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

