A recurrent RNA-binding domain is appended to eukaryotic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
- PMID: 10654942
- PMCID: PMC305581
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.3.445
A recurrent RNA-binding domain is appended to eukaryotic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
Abstract
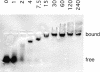
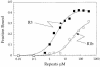
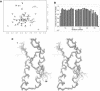
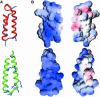
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases of higher eukaryotes possess polypeptide extensions in contrast to their prokaryotic counterparts. These extra domains of poorly understood function are believed to be involved in protein-protein or protein-RNA interactions. Here we showed by gel retardation and filter binding experiments that the repeated units that build the linker region of the bifunctional glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase had a general RNA-binding capacity. The solution structure of one of these repeated motifs was also solved by NMR spectroscopy. One repeat is built around an antiparallel coiled-coil. Strikingly, the conserved lysine and arginine residues form a basic patch on one side of the structure, presenting a suitable docking surface for nucleic acids. Therefore, this repeated motif may represent a novel type of general RNA-binding domain appended to eukaryotic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases to serve as a cis-acting tRNA-binding cofactor.
Figures

References
-
- Alzhanova A.T., Fedorov, A.N., Ovchinnikov, L.P. and Spirin, A.S. (1980) Eukaryotic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are RNA binding proteins whereas prokaryotic ones are not. FEBS Lett., 120, 225–229. - PubMed
-
- Arnez J.G. and Cavarelli, J. (1997) Structures of RNA-binding proteins. Q. Rev. Biophys., 30, 195–240. - PubMed
-
- Berglund H., Rak, A., Serganov, A., Garber, M. and Härd, T. (1997) Solution structure of the ribosomal RNA binding protein S15 from Thermus thermophilus. Nature Struct. Biol., 4, 20–23. - PubMed
-
- Biou V., Yaremchuk, A., Tukalo, M. and Cusack, S. (1994) The 2.9 Å crystal structure of T.thermophilus seryl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNASer. Science, 263, 1404–1410. - PubMed
-
- Brünger A.T. (1993) X-PLOR Version 3.1: A System for X-ray Crystallography and NMR. Yale University Press, New Haven, CT.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

