Specificity and sensitivity of high levels of immunoglobulin G antibodies against pertussis toxin in a single serum sample for diagnosis of infection with Bordetella pertussis
- PMID: 10655388
- PMCID: PMC86208
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.2.800-806.2000
Specificity and sensitivity of high levels of immunoglobulin G antibodies against pertussis toxin in a single serum sample for diagnosis of infection with Bordetella pertussis
Abstract
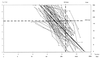
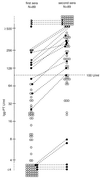
Laboratory confirmation of pertussis by culture, PCR, or detection of antibody increase in paired sera is hampered by low sensitivity in the later stages of the disease. Therefore, we investigated whether, and at which level, concentrations of immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against pertussis toxin (PT), IgG-PT, in a single serum sample are indicative of active or recent pertussis. IgG-PT, measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in units per milliliter, was analyzed in 7,756 sera collected in a population-based study in The Netherlands, in the sera of 3,491 patients with at least a fourfold increase of IgG-PT, in paired sera of 89 patients with positive cultures and/or PCR results, and in the sera of 57 patients with clinically documented pertussis with a median follow-up of 1.4 years. We conclude that, independently of age, IgG-PT levels of at least 100 U/ml are diagnostic of recent or active infection with Bordetella pertussis. Such levels are present in less than 1% of the population and are reached in most pertussis patients within 4 weeks after disease onset and persist only temporarily.
Figures

References
-
- Addiss D G, Davis J P, Meade B D, Burstyn D G, Meissner M, Zastrow J A, Berg J L, Drinka P, Philips R. A pertussis outbreak in a Wisconsin nursing home. J Infect Dis. 1991;164:704–710. - PubMed
-
- Baker J D, Halperin S A, Edwards K, Miller B, Decker M, Stephens D. Antibody response to Bordetella pertussis antigens after immunization with American and Canadian whole-cell vaccines. J Pediatr. 1992;121:523–527. - PubMed
-
- Cattaneo L A, Reed G W, Haase D H, Wills M J, Edwards K M. The seroepidemiology of Bordetella pertussis infections: a study of persons aged 1–65 years. J Infect Dis. 1996;173:1256–1259. - PubMed
-
- Cherry J D. The role of Bordetella pertussis infections in adults in the epidemiology of pertussis. Dev Biol Stand. 1997;89:181–186. - PubMed
-
- Cochran W G. Sampling techniques. 3rd ed. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons; 1997.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

