PCR using 3'-mismatched primers to detect A2142C mutation in 23S rRNA conferring resistance to clarithromycin in Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates
- PMID: 10655418
- PMCID: PMC86249
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.2.923-925.2000
PCR using 3'-mismatched primers to detect A2142C mutation in 23S rRNA conferring resistance to clarithromycin in Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates
Abstract
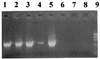
Twenty-five clarithromycin-resistant Helicobacter pylori strains (selected by agar dilution) were studied to detect A2142G and A2143G mutations in the 23S rRNA gene by a PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism method and an A2142C mutation by PCR using a 3'-mismatched specific primer. A 700-bp amplified fragment was obtained by the mismatched PCR only in strains without an A2142G or A2143G mutation, indicating that those strains had the A2142C mutation.
Figures

References
-
- Alarcón T, Domingo D, López-Brea M. Antibiotic resistance problems with Helicobacter pylori. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1999;12:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Debets-Ossenkopp Y J, Sparrius M, Kusters J G, Kolkman J J, Vandenbroucke-Grauls C M J E. Mechanism of clarithromycin resistance in clinical isolates of Helicobacter pylori. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1996;142:37–42. - PubMed
-
- Domingo D, Alarcon T, Sanz J C, Sánchez I, López-Brea M. High frequency of mutations at position 2144 of the 23S rRNA gene in clarithromycin resistant Helicobacter pylori strains isolated in Spain. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998;41:573–574. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

