Positive and negative regulation of endogenous genes by designed transcription factors
- PMID: 10660690
- PMCID: PMC26462
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.040552697
Positive and negative regulation of endogenous genes by designed transcription factors
Abstract
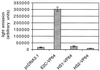
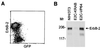
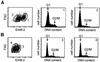
Gene regulation by imposed localization was studied by using designed zinc finger proteins that bind 18-bp DNA sequences in the 5' untranslated regions of the protooncogenes erbB-2 and erbB-3. Transcription factors were generated by fusion of the DNA-binding proteins to repression or activation domains. When introduced into cells these transcription factors acted as dominant repressors or activators of, respectively, endogenous erbB-2 or erbB-3 gene expression. Significantly, imposed regulation of the two genes was highly specific, despite the fact that the transcription factor binding sites targeted in erbB-2 and erbB-3 share 15 of 18 nucleotides. Regulation of erbB-2 gene expression was observed in cells derived from several species that conserve the DNA target sequence. Repression of erbB-2 in SKBR3 breast cancer cells inhibited cell-cycle progression by inducing a G(1) accumulation, suggesting the potential of designed transcription factors for cancer gene therapy. These results demonstrate the willful up- and down-regulation of endogenous genes, and provide an additional means to alter biological systems.
Figures
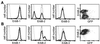

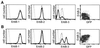
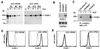
Similar articles
-
Development of zinc finger domains for recognition of the 5'-ANN-3' family of DNA sequences and their use in the construction of artificial transcription factors.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 3;276(31):29466-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102604200. Epub 2001 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11340073
-
Development of zinc finger domains for recognition of the 5'-CNN-3' family DNA sequences and their use in the construction of artificial transcription factors.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 21;280(42):35588-97. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506654200. Epub 2005 Aug 17. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16107335
-
Toward controlling gene expression at will: specific regulation of the erbB-2/HER-2 promoter by using polydactyl zinc finger proteins constructed from modular building blocks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Dec 8;95(25):14628-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.25.14628. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9843940 Free PMC article.
-
A structure-function analysis of transcriptional repression mediated by the WT1, Wilms' tumor suppressor protein.Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1713-20. Oncogene. 1993. PMID: 8510918
-
Zinc finger peptides for the regulation of gene expression.J Mol Biol. 1999 Oct 22;293(2):215-8. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3007. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10529348 Review.
Cited by
-
Biotechnological Advances to Improve Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crops.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 10;23(19):12053. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912053. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc finger transcription factors designed for bispecific coregulation of ErbB2 and ErbB3 receptors: insights into ErbB receptor biology.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Oct;25(20):9082-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.20.9082-9091.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16199884 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genomic approaches to elucidate the role of enhancers during development.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2020 Mar;12(2):e1467. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1467. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 31808313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR-Cas: Converting A Bacterial Defence Mechanism into A State-of-the-Art Genetic Manipulation Tool.Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 Feb 28;8(1):18. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8010018. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30823430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of programmable integrases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 31;106(13):5053-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812502106. Epub 2009 Mar 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19282480 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

