Roscovitine, a specific inhibitor of cellular cyclin-dependent kinases, inhibits herpes simplex virus DNA synthesis in the presence of viral early proteins
- PMID: 10666240
- PMCID: PMC111691
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.5.2107-2120.2000
Roscovitine, a specific inhibitor of cellular cyclin-dependent kinases, inhibits herpes simplex virus DNA synthesis in the presence of viral early proteins
Abstract
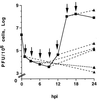
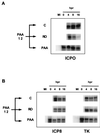
We have previously shown that two inhibitors specific for cellular cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks), Roscovitine (Rosco) and Olomoucine (Olo), block the replication of herpes simplex virus (HSV). Based on these results, we demonstrated that HSV replication requires cellular cdks that are sensitive to these drugs (L. M. Schang, J. Phillips, and P. A. Schaffer. J. Virol. 72:5626-5637, 1998). We further established that at least two distinct steps in the viral replication cycle require cdks: transcription of immediate-early (IE) genes and transcription of early (E) genes (L. M. Schang, A. Rosenberg, and P. A. Schaffer, J. Virol. 73:2161-2172, 1999). Since Rosco inhibits HSV replication efficiently even when added to infected cells at 6 h postinfection, we postulated that cdks may also be required for viral functions that occur after E gene expression. In the study presented herein, we tested this hypothesis directly by measuring the efficiency of viral replication, viral DNA synthesis, and expression of several viral genes during infections in which Rosco was added after E proteins had already been synthesized. Rosco inhibited HSV replication, and specifically viral DNA synthesis, when the drug was added at the time of release from a 12-h phosphonoacetic acid (PAA)-induced block in viral DNA synthesis. Inhibition of DNA synthesis was not a consequence of inhibition of expression of IE or E genes in that Rosco had no effect on steady-state levels of two E transcripts under the same conditions in which it inhibited viral DNA synthesis. Moreover, viral DNA synthesis was inhibited by Rosco even in the absence of protein synthesis. In a second series of experiments, the replication of four HSV mutants harboring temperature-sensitive mutations in genes essential for viral DNA replication was inhibited when Rosco was added at the time of shift-down from the nonpermissive to the permissive temperature. Viral DNA synthesis was inhibited by Rosco under these conditions, whereas expression of viral E genes was not affected. We conclude that cellular Rosco-sensitive cdks are required for replication of viral DNA in the presence of viral E proteins. This requirement may indicate that HSV DNA synthesis is functionally linked to transcription, which requires cdks, or that both viral transcription and DNA replication, independently, require viral or cellular factors activated by Rosco-sensitive cdks.
Figures
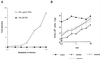

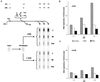



Similar articles
-
Transcription of herpes simplex virus immediate-early and early genes is inhibited by roscovitine, an inhibitor specific for cellular cyclin-dependent kinases.J Virol. 1999 Mar;73(3):2161-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.3.2161-2172.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9971799 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement for cellular cyclin-dependent kinases in herpes simplex virus replication and transcription.J Virol. 1998 Jul;72(7):5626-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.7.5626-5637.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9621021 Free PMC article.
-
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor roscovitine inhibits the transactivating activity and alters the posttranslational modification of herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0.J Virol. 2002 Feb;76(3):1077-88. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.3.1077-1088.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11773384 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of pharmacological cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors on viral transcription and replication.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 11;1697(1-2):197-209. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2003.11.024. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15023361 Review.
-
Cdk inhibitory nucleoside analogs prevent transcription from viral genomes.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2005;24(5-7):829-37. doi: 10.1081/ncn-200060314. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2005. PMID: 16248044 Review.
Cited by
-
Centromere architecture breakdown induced by the viral E3 ubiquitin ligase ICP0 protein of herpes simplex virus type 1.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44227. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044227. Epub 2012 Sep 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028505 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression analyzed by microarrays in HSV-1 latent mouse trigeminal ganglion following heat stress.Virus Genes. 2001 Dec;23(3):273-80. doi: 10.1023/a:1012517221937. Virus Genes. 2001. PMID: 11778695
-
Use of a multi-virus array for the study of human viral and retroviral pathogens: gene expression studies and ChIP-chip analysis.Retrovirology. 2004 May 25;1:10. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-1-10. Retrovirology. 2004. PMID: 15169557 Free PMC article.
-
Remote Activation of Host Cell DNA Synthesis in Uninfected Cells Signaled by Infected Cells in Advance of Virus Transmission.J Virol. 2015 Nov;89(21):11107-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01950-15. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26311877 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivation of lytic replication from B cells latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus occurs with high S-phase cyclin-dependent kinase activity while inhibiting cellular DNA replication.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(2):851-61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.2.851-861.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12502801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham R T, Acquarone M, Andersen A, Asensi A, Belle R, Berger F, Bergounioux C, Brunn G, Buquet-Fagot C, Fagot D, et al. Cellular effects of olomoucine, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. Biol Cell. 1995;83:105–120. - PubMed
-
- Alessi F, Quarta S, Savio M, Riva F, Rossi L, Stivala L, Scovassi A, Meijer L, Prosperi E. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors olomoucine and roscovitine arrest human fibroblasts in G1 phase by specific inhibition of CDK2 kinase activity. Exp Cell Res. 1998;245:8–18. - PubMed
-
- Becker Y, Asher Y, Cohen Y, Weinberg-Zahlering E, Shlomai J. Phosphonoacetic acid-resistant mutants of herpes simplex virus: effect of phosphonoacetic acid on virus replication and in vitro deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in isolated nuclei. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1997;11:919–922. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beijersbergen R L, Carlee L, Kerkhoven R M, Bernards R. Regulation of the retinoblastoma protein-related p107 by G1 cyclin complexes. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1340–1353. - PubMed
-
- Bohemer P E, Lehman I. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1997;66:347–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

