Identification of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase as a transcriptional coactivator of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein
- PMID: 10666246
- PMCID: PMC111697
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.5.2169-2177.2000
Identification of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase as a transcriptional coactivator of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein
Abstract
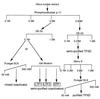
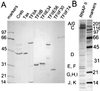
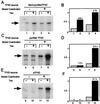
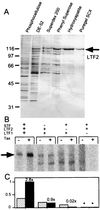
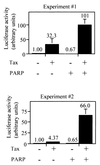
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) encodes a transcriptional activator, Tax, whose activity is believed to contribute significantly to cellular transformation. Tax stimulates transcription from the proviral promoter as well as from promoters for a variety of cellular genes. The mechanism through which Tax communicates to the general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II has not been completely determined. We investigated whether Tax could function directly through the general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II or if other intermediary factors or coactivators were required. Our results show that a system consisting of purified recombinant TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIIE, TFIIF, CREB, and Tax, along with highly purified RNA polymerase II, affinity-purified epitope-tagged TFIID, and semipurified TFIIH, supports basal transcription of the HTLV-1 promoter but is not responsive to Tax. Two additional activities were required for Tax to stimulate transcription. We demonstrate that one of these activities is poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), a molecule that has been previously identified to be the transcriptional coactivator PC1. PARP functions as a coactivator in our assays at molar concentrations approximately equal to those of the DNA and equal to or less than those of the transcription factors in the assay. We further demonstrate that PARP stimulates Tax-activated transcription in vivo, demonstrating that this biochemical approach has functionally identified a novel target for the retroviral transcriptional activator Tax.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sequence-specific binding of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 to the human T cell leukemia virus type-I tax responsive element.Virology. 2002 Apr 25;296(1):107-16. doi: 10.1006/viro.2002.1385. Virology. 2002. PMID: 12036322
-
Acetylation of nucleosomal histones by p300 facilitates transcription from tax-responsive human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 chromatin template.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;22(13):4450-62. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.13.4450-4462.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12052856 Free PMC article.
-
Transactivation of the human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax1-responsive 21-base-pair repeats requires Holo-TFIID and TFIIA.J Virol. 1995 Aug;69(8):5077-86. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.8.5077-5086.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7609077 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the tumor suppressor function of CBP through the viral oncoprotein tax.Gene Expr. 2000;9(1-2):29-36. doi: 10.3727/000000001783992678. Gene Expr. 2000. PMID: 11097423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Adult T-cell leukemia induced by HTLV-1: before and after HBZ].Med Sci (Paris). 2010 Apr;26(4):391-6. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2010264391. Med Sci (Paris). 2010. PMID: 20412744 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Identification of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 as a cell cycle regulator through modulating Sp1 mediated transcription in human hepatoma cells.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 19;8(12):e82872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082872. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24367566 Free PMC article.
-
PMA-induced dissociation of Ku86 from the promoter causes transcriptional up-regulation of histamine H(1) receptor.Sci Rep. 2012;2:916. doi: 10.1038/srep00916. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Sci Rep. 2012. PMID: 23209876 Free PMC article.
-
Dual regulation of AP-2alpha transcriptional activation by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1.Biochem J. 2004 Aug 15;382(Pt 1):323-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040593. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15170387 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleosomes containing the histone variant H2A.Bbd organize only 118 base pairs of DNA.EMBO J. 2004 Aug 18;23(16):3314-24. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600316. Epub 2004 Jul 15. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15257289 Free PMC article.
-
p300-mediated tax transactivation from recombinant chromatin: histone tail deletion mimics coactivator function.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jan;22(1):127-37. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.1.127-137.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11739728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson M G, Matthews M-A M, Dynan W S. In vitro binding and transcription assays using the human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein. In: Adolph K W, editor. Viral gene techniques. Vol. 7. San Diego, Calif: Academic Press; 1995. pp. 267–279.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

