A chimeric protein containing the N terminus of the adeno-associated virus Rep protein recognizes its target site in an in vivo assay
- PMID: 10666268
- PMCID: PMC111719
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.5.2372-2382.2000
A chimeric protein containing the N terminus of the adeno-associated virus Rep protein recognizes its target site in an in vivo assay
Abstract
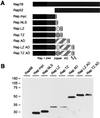
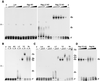
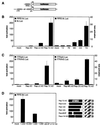
The Rep78 and Rep68 proteins of adeno-associated virus (AAV) type 2 are involved in DNA replication, regulation of gene expression, and targeting site-specific integration. They bind to a specific Rep recognition sequence (RRS) found in both the viral inverted terminal repeats and the AAVS1 integration locus on human chromosome 19. Previous in vitro studies implied that an N-terminal segment of Rep is involved in DNA recognition, while additional domains might stabilize binding and mediate multimerization. In order to define the minimal requirements for Rep to recognize its target site in the human genome, we developed one-hybrid assays in which DNA-protein interactions are detected in vivo. Chimeric proteins consisting of the N terminus of Rep fused to different oligomerization motifs and a transcriptional activation domain were analyzed for oligomerization, DNA binding, and activation of reporter gene expression. Expression of reporter genes was driven from RRS motifs cloned upstream of minimal promoters and examined in mammalian cells from transfected plasmids and in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from a reporter cassette integrated into the yeast genome. Our results show for the first time that chimeric proteins containing the amino-terminal 244 residues of Rep are able to target the RRS in vitro and in vivo when incorporated into artificial multimers. These studies suggest that chimeric proteins may be used to harness the unique targeting feature of AAV for gene therapy applications.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1/adeno-associated virus hybrid vectors mediate site-specific integration at the adeno-associated virus preintegration site, AAVS1, on human chromosome 19.J Virol. 2002 Jul;76(14):7163-73. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.14.7163-7173.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12072516 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulation of the adeno-associated virus (AAV) P5 promoter involves both the P5 rep binding site and the consensus ATP-binding motif of the AAV Rep68 protein.J Virol. 1995 Nov;69(11):6787-96. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.11.6787-6796.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7474090 Free PMC article.
-
A Rep recognition sequence is necessary but not sufficient for nicking of DNA by adeno-associated virus type-2 Rep proteins.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001 May 15;389(2):271-7. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2001.2348. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11339817
-
Binding sites for adeno-associated virus Rep proteins within the human genome.J Virol. 1997 Mar;71(3):2528-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.3.2528-2534.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9032395 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of AAV Rep proteins in gene expression and targeted integration.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996;218:25-33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-80207-2_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8794243 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Rescue of DNA-PK Signaling and T-Cell Differentiation by Targeted Genome Editing in a prkdc Deficient iPSC Disease Model.PLoS Genet. 2015 May 22;11(5):e1005239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005239. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26000857 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of adeno-associated virus type 2 Rep40-ADP complex: insight into nucleotide recognition and catalysis by superfamily 3 helicases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Aug 24;101(34):12455-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403454101. Epub 2004 Aug 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15310852 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient expression of the adeno-associated virus type 5 p41 capsid gene promoter in 293 cells does not require Rep.J Virol. 2006 Jul;80(13):6559-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00387-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16775342 Free PMC article.
-
Adeno-Associated Virus Genome Interactions Important for Vector Production and Transduction.Hum Gene Ther. 2020 May;31(9-10):499-511. doi: 10.1089/hum.2020.069. Hum Gene Ther. 2020. PMID: 32303138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Expression and Function of the Small Nonstructural Proteins of Adeno-Associated Viruses (AAVs).Viruses. 2024 Jul 29;16(8):1215. doi: 10.3390/v16081215. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39205189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Batchu R B, Kotin R M, Hermonat P L. The regulatory Rep protein of adeno-associated virus binds to sequences within the c-H-ras promoter. Cancer Lett. 1994;86:23–31. - PubMed
-
- Berns K I. Parvoviridae: the viruses and their replication. In: Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, editors. Fields virology. 3rd ed. Vol. 2. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott-Raven Publishers; 1996. pp. 2173–2197.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

