Epstein-Barr virus entry utilizing HLA-DP or HLA-DQ as a coreceptor
- PMID: 10666279
- PMCID: PMC111730
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.5.2451-2454.2000
Epstein-Barr virus entry utilizing HLA-DP or HLA-DQ as a coreceptor
Abstract
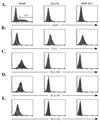
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) glycoprotein gp350/gp220 association with cellular CD21 facilitates virion attachment to B lymphocytes. Membrane fusion requires the additional interaction between virion gp42 and cellular HLA-DR. This binding is thought to catalyze membrane fusion through a further association with the gp85-gp25 (gH-gL) complex. Cell lines expressing CD21 but lacking expression of HLA class II molecules are resistant to infection by a recombinant EBV expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein. Surface expression of HLA-DR, HLA-DP, or HLA-DQ confers susceptibility to EBV infection on resistant cells that express CD21. Therefore, HLA-DP or HLA-DQ can substitute for HLA-DR and serve as a coreceptor in EBV entry.
Figures

References
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Basham T, Smith W, Lanier L, Morhenn V, Merigan T. Regulation of expression of class II major histocompatibility antigens on human peripheral blood monocytes and Langerhans cells by interferon. Hum Immunol. 1984;10:83–93. - PubMed
-
- Basta P V, Sherman P A, Ting J P. Identification of an interferon-gamma response region 5′ of the human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen DR alpha chain gene which is active in human glioblastoma multiforme lines. J Immunol. 1987;138:1275–1280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

