Adeno-associated virus major Rep78 protein disrupts binding of TATA-binding protein to the p97 promoter of human papillomavirus type 16
- PMID: 10666281
- PMCID: PMC111732
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.5.2459-2465.2000
Adeno-associated virus major Rep78 protein disrupts binding of TATA-binding protein to the p97 promoter of human papillomavirus type 16
Abstract
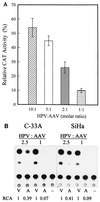
Adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV) is known to inhibit the promoter activities of several oncogenes and viral genes, including the human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV-16) E6 and E7 transforming genes. However, the target elements of AAV on the long control region (LCR) upstream of E6 and E7 oncogenes are elusive. A chloramphenicol acetyltransferase assay was performed to study the effect of AAV on the transcription activity of the HPV-16 LCR in SiHa (HPV-positive) and C-33A (HPV-negative) cells. The results reveal that (i) AAV inhibited HPV-16 LCR activity in a dose-dependent manner, (ii) AAV-mediated inhibition did not require the HPV gene products, and (iii) the AAV replication gene product Rep78 was involved in the inhibition. Deletion mutation analyses of the HPV-16 LCR showed that regulatory elements outside the core promoter region of the LCR may not be direct targets of AAV-mediated inhibition. Further study with the electrophoretic mobility shift assay demonstrated that Rep78 interfered with the binding of TATA-binding protein (TBP) to the TATA box of the p97 core promoter more significantly than it disrupted the preformed TBP-TATA complex. These data thus suggest that Rep78 may inhibit transcription initiation of the HPV-16 LCR by disrupting the interaction between TBP and the TATA box of the p97 core promoter.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Binding of the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein and the adeno-associated virus Rep78 major regulatory protein in vitro and in yeast and the potential for downstream effects.J Hum Virol. 2000 May-Jun;3(3):113-24. J Hum Virol. 2000. PMID: 10881991
-
Binding of the human papillomavirus type 16 p97 promoter by the adeno-associated virus Rep78 major regulatory protein correlates with inhibition.J Biol Chem. 1999 Oct 29;274(44):31619-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.44.31619. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10531369
-
The adeno-associated virus major regulatory protein Rep78-c-Jun-DNA motif complex modulates AP-1 activity.Virology. 2003 Sep 15;314(1):423-31. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00439-2. Virology. 2003. PMID: 14517094
-
Adeno-associated virus Rep78 binds to E2-responsive element 1 of bovine papillomavirus type 1.IUBMB Life. 1999 Oct;48(4):397-404. doi: 10.1080/713803543. IUBMB Life. 1999. PMID: 10632568
-
Mutational analysis of adeno-associated virus Rep protein-mediated inhibition of heterologous and homologous promoters.J Virol. 1995 Sep;69(9):5485-96. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.9.5485-5496.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7636994 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of adeno-associated virus on adenovirus replication and gene expression during coinfection.J Virol. 2006 Aug;80(16):7807-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00198-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16873238 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an adeno-associated virus Rep protein binding site in the adenovirus E2a promoter.J Virol. 2005 Jan;79(1):28-38. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.28-38.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15596798 Free PMC article.
-
Studies of the mechanism of transactivation of the adeno-associated virus p19 promoter by Rep protein.J Virol. 2002 Aug;76(16):8225-35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.16.8225-8235.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12134028 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2003 Jan;16(1):1-17. doi: 10.1128/CMR.16.1.1-17.2003. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2003. PMID: 12525422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adeno-associated virus type 2 rep protein inhibits human papillomavirus type 16 E2 recruitment of the transcriptional coactivator p300.J Virol. 2000 Oct;74(19):9090-8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.19.9090-9098.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10982355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apt D, Watts R M, Suske G, Bernard H U. High Sp1/Sp3 ratios in epithelial cells during epithelial differentiation and cellular transformation correlate with the activation of the HPV-16 promoter. Virology. 1996;224:281–291. - PubMed
-
- Berns K I. Parvoviridae: the viruses and their replication. In: Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, editors. Fields virology. 3rd ed. Vol. 2. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott-Raven; 1996. pp. 2173–2197.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

