Vasculogenic mimicry and tumor angiogenesis
- PMID: 10666364
- PMCID: PMC1850026
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64739-6
Vasculogenic mimicry and tumor angiogenesis
Abstract
Tumors require a blood supply for growth and hematogenous dissemination. Much attention has been focused on the role of angiogenesis-the recruitment of new vessels into a tumor from pre-existing vessels. However, angiogenesis may not be the only mechanism by which tumors acquire a microcirculation. Highly aggressive and metastatic melanoma cells are capable of forming highly patterned vascular channels in vitro that are composed of a basement membrane that stains positive with the periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) reagent in the absence of endothelial cells and fibroblasts. These channels formed in vitro are identical morphologically to PAS-positive channels in histological preparations from highly aggressive primary uveal melanomas, in the vertical growth phase of cutaneous melanomas, and in metastatic uveal and cutaneous melanoma. The generation of microvascular channels by genetically deregulated, aggressive tumor cells was termed "vasculogenic mimicry" to emphasize their de novo generation without participation by endothelial cells and independent of angiogenesis. Techniques designed to identify the tumor microcirculation by the staining of endothelial cells may not be applicable to tumors that express vasculogenic mimicry. Although it is not known if therapeutic strategies targeting endothelial cells will be effective in tumors whose blood supply is formed by tumor cells in the absence of angiogenesis, the biomechanical and molecular events that regulate vasculogenic mimicry provide opportunities for the development of novel forms of tumor-targeted treatments. The unique patterning characteristic of vasculogenic mimicry provides an opportunity to design noninvasive imaging techniques to detect highly aggressive neoplasms and their metastases.
Figures
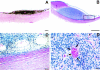



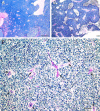
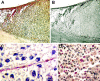
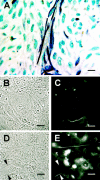



Comment in
-
Vasculogenic mimicry in tumors. Fact or artifact?Am J Pathol. 2000 Feb;156(2):359. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64738-4. Am J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10666363 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 1997, 386:671-674 - PubMed
-
- Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 1971, 285:1182-1186 - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Folkman J: Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 1996, 86:353-364 - PubMed
-
- Fukumura D, Xavier R, Sugiura T, Chen Y, Park EC, Lu NF, Selig M, Nielsen G, Taksir T, Jain RK, Seed B: Tumor induction of VEGF promotor activity in stromal cells. Cell 1998, 94:715-725 - PubMed
-
- Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, Silver M, van der ZR, Li T, Witzenbichler B, Schatteman G, Isner JM: Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 1997, 275:964–967 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

