Retinopathy and nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes four years after a trial of intensive therapy
- PMID: 10666428
- PMCID: PMC2630213
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJM200002103420603
Retinopathy and nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes four years after a trial of intensive therapy
Erratum in
- N Engl J Med 2000 May 4;342(18):1376
Abstract
Background: Among patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, intensive therapy (with the aim of achieving near-normal blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin concentrations [hemoglobin A1c]) markedly reduces the risk of microvascular complications as compared with conventional therapy. To assess whether these benefits persist, we compared the effects of former and intensive conventional therapy on the recurrence and severity of retinopathy and nephropathy for four years after the end of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT).
Methods: At the end of the DCCT, the patients in the conventional-therapy group were offered intensive therapy, and the care of all patients was transferred to their own physicians. Retinopathy was evaluated on the basis of centrally graded fundus photographs in 1208 patients during the fourth year after the DCCT ended, and nephropathy was evaluated on the basis of urine specimens obtained from 1302 patients during the third or fourth year, approximately half of whom were from each treatment group.
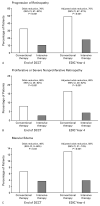
Results: The difference in the median glycosylated hemoglobin values between the conventional-therapy and intensive-therapy groups during the 6.5 years of the DCCT (average, 9.1 percent and 7.2 percent, respectively) narrowed during follow-up (median during 4 years, 8.2 percent and 7.9 percent, respectively, P<0.001). Nevertheless, the proportion of patients who had worsening retinopathy, including proliferative retinopathy, macular edema, and the need for laser therapy, was lower in the intensive-therapy group than in the conventional-therapy group (odds reduction, 72 percent to 87 percent, P<0.001). The proportion of patients with an increase in urinary albumin excretion was significantly lower in the intensive-therapy group.
Conclusions: The reduction in the risk of progressive retinopathy and nephropathy resulting from intensive therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes persists for at least four years, despite increasing hyperglycemia.
Figures


References
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive therapy of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–86. - PubMed
-
- Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) Research Group Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC): design, implementation, and preliminary results of a long-term follow-up of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial cohort. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:99–111. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group Fundus photographic risk factors for progression of diabetic retinopathy: ETDRS report number 12. Ophthalmology. 1991;98(Suppl):823–33. - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive diabetes treatment on the progression of diabetic retinopathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995;113:36–51. - PubMed
-
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group Photocoagulation for diabetic macular edema: Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study report number 1. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985;103:1796–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
