Sequential requirements of the N-terminal palmitoylation site and SH2 domain of Src family kinases in the initiation and progression of FcepsilonRI signaling
- PMID: 10669752
- PMCID: PMC85358
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.5.1759-1771.2000
Sequential requirements of the N-terminal palmitoylation site and SH2 domain of Src family kinases in the initiation and progression of FcepsilonRI signaling
Abstract
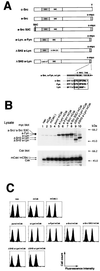
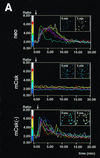
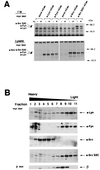
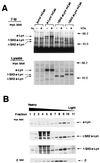
Initial biochemical signaling originating from high-affinity immunoglobulin E receptor (FcepsilonRI) has been ascribed to Src family kinases. To understand the mechanisms by which individual kinases drive the signaling, we conducted reconstitution experiments: FcepsilonRI signaling in RBL2H3 cells was first suppressed by a membrane-anchored, gain-of-function C-terminal Src kinase and then reconstructed with Src family kinases whose C-terminal negative regulatory sequence was replaced with a c-myc epitope. Those constructs derived from Lyn and Fyn, which are associated with detergent-resistant membranes (DRMs), physically interacted with resting FcepsilonRI and reconstructed clustering-induced signaling that leads to calcium mobilization and ERK1 and -2 activation. c-Src-derived construct, which was excluded from DRMs, failed to interact with FcepsilonRI and to restore the signaling, whereas creation of palmitoylatable Cys3 enabled it to interact with DRMs and with FcepsilonRI and to restore the signaling. Deletion of Src homology 3 (SH3) domain from the Lyn-derived construct did not alter its ability to transduce the series of signaling. Deletion of SH2 domain did not affect its association with DRMs and with FcepsilonRI nor clustering-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of FcepsilonRI beta and gamma subunits, but it almost abrogated the next step of tyrosine phosphorylation of Syk and its recruitment to FcepsilonRI. These findings suggest that Lyn and Fyn could, but c-Src could not, drive FcepsilonRI signaling and that N-terminal palmitoylation and SH2 domain are required in sequence for the initial interaction with FcepsilonRI and for the signal progression to the molecular assembly.
Figures

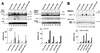
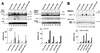
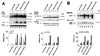
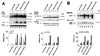

References
-
- Amoui M, Draberova L, Tolar P, Draber P. Direct interaction of Syk and Lyn protein tyrosine kinases in rat basophilic leukemia cells activated via type I Fcɛ receptors. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:321–328. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y, Kim Y T, Stillwell R, Kim T J, Pillai S. The SH2 domains of Src family kinases associate with Syk. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:15658–15663. - PubMed
-
- Beaven M A, Metzger H. Signal transduction by Fc receptors: the FcɛRI case. Immunol Today. 1993;14:222–226. - PubMed
-
- Benhamou M, Ryba N J, Kihara H, Nishikata H, Siraganian R P. Protein-tyrosine kinase p72syk in high affinity IgE receptor signaling. Identification as a component of pp72 and association with the receptor γ chain after receptor aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:23318–23324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
