The neuron-enriched splicing pattern of Drosophila erect wing is dependent on the presence of ELAV protein
- PMID: 10669758
- PMCID: PMC85364
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.5.1836-1845.2000
The neuron-enriched splicing pattern of Drosophila erect wing is dependent on the presence of ELAV protein
Abstract
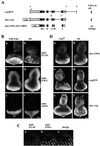
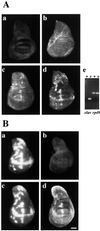
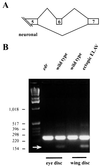
Although the Drosophila melanogaster erect wing (ewg) gene is broadly transcribed in adults, an unusual posttranscriptional regulation involving alternative and inefficient splicing generates a 116-kDa EWG protein in neurons, while protein expression elsewhere or of other isoforms is below detection at this stage. This posttranscriptional control is important, as broad expression of EWG can be lethal. In this paper, we show that ELAV, a neuron-specific RNA binding protein, is necessary to regulate EWG protein expression in ELAV-null eye imaginal disc clones and that ELAV is sufficient for EWG expression in wing disc imaginal tissue after ectopic expression. Further, analysis of EWG expression elicited from intron-containing genomic transgenes and cDNA minitransgenes in ELAV-deficient eye discs shows that this regulation is dependent on the presence of ewg introns. Analyses of the ewg splicing patterns in wild-type and ELAV-deficient eye imaginal discs and in wild-type and ectopic ELAV-expressing wing imaginal discs, show that certain neuronal splice isoforms correspond to ELAV levels. The data presented in this paper are consistent with a mechanism in which ELAV increases the splicing efficiency of ewg transcripts in alternatively spliced regions rather than with a mechanism in which stability of specific splice forms is enhanced by ELAV. Additionally, we report that ELAV promotes a neuron-enriched splice isoform of Drosophila armadillo transcript. ELAV, however, is not involved in all neuron-enriched splice events.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ELAV inhibits 3'-end processing to promote neural splicing of ewg pre-mRNA.Genes Dev. 2003 Oct 15;17(20):2526-38. doi: 10.1101/gad.1106703. Epub 2003 Oct 1. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 14522950 Free PMC article.
-
Differential and inefficient splicing of a broadly expressed Drosophila erect wing transcript results in tissue-specific enrichment of the vital EWG protein isoform.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Jun;19(6):3998-4007. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.6.3998. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10330140 Free PMC article.
-
ELAV, a Drosophila neuron-specific protein, mediates the generation of an alternatively spliced neural protein isoform.Curr Biol. 1996 Dec 1;6(12):1634-41. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)70787-2. Curr Biol. 1996. PMID: 8994828
-
Determinants of ELAV gene-specific regulation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Aug;38(4):1122-4. doi: 10.1042/BST0381122. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20659015 Review.
-
Regulation of neuronal RNA signatures by ELAV/Hu proteins.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Mar;14(2):e1733. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1733. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 35429136 Review.
Cited by
-
A functional genomic screen in planarians identifies novel regulators of germ cell development.Genes Dev. 2010 Sep 15;24(18):2081-92. doi: 10.1101/gad.1951010. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20844018 Free PMC article.
-
ELAV inhibits 3'-end processing to promote neural splicing of ewg pre-mRNA.Genes Dev. 2003 Oct 15;17(20):2526-38. doi: 10.1101/gad.1106703. Epub 2003 Oct 1. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 14522950 Free PMC article.
-
A critical developmental window for ELAV/Hu-dependent mRNA signatures at the onset of neuronal differentiation.Cell Rep. 2022 Oct 25;41(4):111542. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111542. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36288718 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-binding protein ELAV regulates Hox RNA processing, expression and function within the Drosophila nervous system.Development. 2014 May;141(10):2046-56. doi: 10.1242/dev.101519. Development. 2014. PMID: 24803653 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Elav-like (Hu) proteins regulate RNA splicing and abundance to control glutamate levels and neuronal excitability.Neuron. 2012 Sep 20;75(6):1067-80. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.07.009. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 22998874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams M D, Tarng R S, Rio D C. The alternative splicing factor PSI regulates P-element third intron splicing in vivo. Genes Dev. 1997;11:129–138. - PubMed
-
- Baker B S. Sex in flies: the splice of life. Nature. 1989;340:521–524. - PubMed
-
- Bashaw G J, Baker B S. The regulation of the Drosophila msl-2 gene reveals a function for Sex-lethal in translational control. Cell. 1997;89:789–798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
