Non-linear pharmacokinetics of MDMA ('ecstasy') in humans
- PMID: 10671903
- PMCID: PMC2014905
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2000.00121.x
Non-linear pharmacokinetics of MDMA ('ecstasy') in humans
Abstract
Aims: 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, commonly called ecstasy) is a synthetic compound increasingly popular as a recreational drug. Little is known about its pharmacology, including its metabolism and pharmacokinetics, in humans in controlled settings. A clinical trial was designed for the evaluation of MDMA pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers.
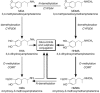
Methods: A total of 14 subjects were included. In the pilot phase six received MDMA at 50 (n=2), 100 (n=2), and 150 mg (n=2). In the second phase eight received MDMA at both 75 and 125 mg (n=8). Subjects were phenotyped for CYP2D6 activity and were classified as extensive metabolizers for substrates, such as MDMA, whose hepatic metabolism is regulated by this enzyme. Plasma and urine samples were collected throughout the study for the evaluation of MDMA pharmacokinetics. Body fluids were analysed for the determination of MDMA and its main metabolites 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA), 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-methamphetamine (HMMA) and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-amphetamine (HMA).
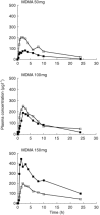
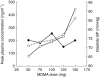
Results: As the dose of MDMA administered was increased, volunteers showed rises in MDMA concentrations that did not follow the same proportionality which could be indicative of nonlinearity. In the full range of doses tested the constant recovery of HMMA in the urine combined with the increasing MDMA recovery seems to point towards a saturation or an inhibition of MDMA metabolism (the demethylenation step). These observations are further supported by the fact that urinary clearance was rather constant while nonrenal clearance was dose dependent.
Conclusions: It has previously been postulated that individuals genetically deficient for the hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 (about 10% of the Caucasian people) were at risk of developing acute toxicity at moderate doses of MDMA because the drug would accumulate in the body instead of being metabolized and inactivated. The lack of linearity of MDMA pharmacokinetics (in a window of doses compatible with its recreational use) is a more general phenomenon as it concerns the whole population independent of their CYP2D6 genotype. It implies that relatively small increases in the dose of MDMA ingested are translated to disproportionate rises in MDMA plasma concentrations and hence subjects are more prone to develop acute toxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Nichols DE. Differences between the mechanism of action of MDMA, MBDB and the classic hallucinogens. Identification of a new therapeutic class: Entactogens. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1986;18:305–313. - PubMed
-
- Henry JA, Jeffregsand KS, Loumberg W. Toxicity and deaths from 3, 4–methylenedioxymethamphetamine. Lancet. 1992;340:384–387. - PubMed
-
- Spanos LJ, Yamamoto BK. Acute and subchronic effects of methylenedioxy methamphetamine (±MDMA) on locomotion and serotonin syndrome in rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1989;32:835–840. - PubMed
-
- Burdkin J, Malyala A, Nash JF. Effect of acute monoamine depletion on 3, 4–methylenedioxymethamphetamine–induced neurotoxicity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1993;45:647–653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

