Human intestinal epithelial cells secrete interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-8 but not interleukin-1 or interleukin-6
- PMID: 10673296
- PMCID: PMC1727863
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.46.3.350
Human intestinal epithelial cells secrete interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-8 but not interleukin-1 or interleukin-6
Abstract
Background: There is growing evidence that intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) are involved in the mucosal immune system.
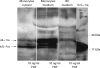
Aim: To assess the pattern of cytokines secreted by IECs and lamina propria mononuclear cells (LPMNCs). To achieve this, the expression and secretion of interleukin (IL)-1, IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra), IL-6, and IL-8 in human primary colonic and ileal IECs and LPMNCs from the same patient were studied.
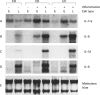
Methods: IECs and LPMNCs were isolated from surgical specimens or endoscopic biopsy samples. mRNA expression was investigated by northern blot analysis. Secretion of IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-1ra was measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay.
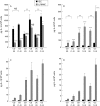
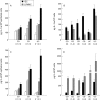
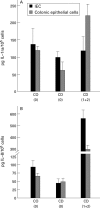
Results: IL-1ra mRNA levels were higher in IECs than in LPMNCs in all probands. IL-8 mRNA was only present in low amounts in the IECs from two controls. In none of the specimens were IL-1beta and IL-6 mRNA present in IECs. Transcripts encoding IL-1beta, IL-1ra, IL-6, and IL-8 were identified in LPMNC preparations of all specimens. IECs from normal mucosa produced no detectable amounts of IL-1beta or IL-6, whereas LPMNCs did. IECs secreted some IL-8 (65 (9) pg/10(5) cells) but significantly more was generated by LPMNCs (408 (43) pg/10(5) cells, p<0.0001). However, IECs secreted more IL-1ra than did LPMNCs (120 (12) v 94 (11) pg/10(5) cells). In acute inflammation, IEC IL-1ra secretion was significantly increased. A correlation between secreted IL-1ra and the macroscopical degree of inflammation was found in Crohn's disease (r = 0.64, p<0.0001, n = 36) and ulcerative colitis (r = 0. 76, p<0.0001, n = 24).
Conclusions: IECs from normal mucosa express and secrete IL-1ra and low amounts of IL-8, but no IL-1 or IL-6. In inflamed mucosa the secretion of IL-1ra by IECs is slightly increased but may be not sufficient to antagonise the greatly increased production of proinflammatory cytokines by LPMNCs and the IECs themselves.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
