Influence of hepatitis delta virus infection on morbidity and mortality in compensated cirrhosis type B. The European Concerted Action on Viral Hepatitis (Eurohep)
- PMID: 10673308
- PMCID: PMC1727859
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.46.3.420
Influence of hepatitis delta virus infection on morbidity and mortality in compensated cirrhosis type B. The European Concerted Action on Viral Hepatitis (Eurohep)
Abstract
Background: The effect of hepatitis delta virus (HDV) infection on the clinical course of cirrhosis type B is poorly defined.
Aims: To investigate the impact of HDV status on morbidity and mortality in cirrhosis type B.
Patients/methods: Retrospective cohort study of 200 Western European patients with compensated cirrhosis type B followed for a median period of 6.6 years.
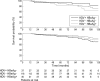
Results: At diagnosis, 20% of patients had antibodies to HDV (anti-HDV); median age was lower in anti-HDV positive cirrhotics (34 v 48 years respectively). Kaplan-Meier five year probability of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was 6, 10, and 9% in anti-HDV positive/HBeAg negative, anti-HDV negative/HBeAg negative, and anti-HDV negative/HBeAg positive cirrhotics respectively; the corresponding figures for decompensation were 22, 16, and 19% and for survival they were 92, 89, and 83% respectively. Cox regression analysis identified age, albumin concentration, gamma-globulin concentration, and HDV status as significant independent prognostic variables. After adjustment for clinical and serological differences at baseline, the risk (95% confidence interval) for HCC, decompensation, and mortality was increased by a factor of 3.2 (1.0 to 10), 2.2 (0.8 to 5.7), and 2.0 (0.7 to 5.7) respectively in anti-HDV positive relative to HDV negative cirrhotic patients. The adjusted estimated five year risk for HCC was 13, 4, and 2% for anti-HDV positive/HBeAg negative, anti-HDV negative/HBeAg negative, and anti-HDV negative/HBeAg positive cirrhotics respectively; the corresponding figures for decompensation were 18, 8, and 14% and for survival 90, 95, and 93% respectively.
Conclusions: HDV infection increases the risk for HCC threefold and for mortality twofold in patients with cirrhosis type B.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
