Chk2/hCds1 functions as a DNA damage checkpoint in G(1) by stabilizing p53
- PMID: 10673500
- PMCID: PMC316357
Chk2/hCds1 functions as a DNA damage checkpoint in G(1) by stabilizing p53
Abstract
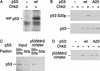
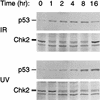
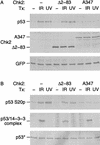
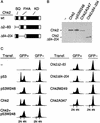
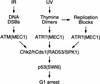
Chk2/hcds1, the human homolog of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD53/SPK1 and Schizosaccharomyces pombe cds1 DNA damage checkpoint genes, encodes a protein kinase that is post-translationally modified after DNA damage. Like its yeast homologs, the Chk2/hCds1 protein phosphorylates Cdc25C in vitro, suggesting that it arrests cells in G(2) in response to DNA damage. We expressed Chk2/hCds1 in human cells and analyzed their cell cycle profile. Wild-type, but not catalytically inactive, Chk2/hCds1 led to G(1) arrest after DNA damage. The arrest was inhibited by cotransfection of a dominant-negative p53 mutant, indicating that Chk2/hCds1 acted upstream of p53. In vitro, Chk2/hCds1 phosphorylated p53 on Ser-20 and dissociated preformed complexes of p53 with Mdm2, a protein that targets p53 for degradation. In vivo, ectopic expression of wild-type Chk2/hCds1 led to increased p53 stabilization after DNA damage, whereas expression of a dominant-negative Chk2/hCds1 mutant abrogated both phosphorylation of p53 on Ser-20 and p53 stabilization. Thus, in response to DNA damage, Chk2/hCds1 stabilizes the p53 tumor suppressor protein leading to cell cycle arrest in G(1).
Figures


References
-
- Banin S, Moyal L, Shieh S, Taya Y, Anderson CW, Chessa L, Smorodinsky NI, Prives C, Reiss Y, Shiloh Y, Ziv Y. Enhanced phosphorylation of p53 by ATM in response to DNA damage. Science. 1998;281:1674–1677. - PubMed
-
- Bell DW, Varley JM, Szydlo TE, Kang DH, Wahrer DC, Shannon KE, Lubratovich M, Verselis SJ, Isselbacher KJ, Fraumeni JF, et al. Heterozygous germline hChk2 mutations in Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Science. 1999;286:2528–2531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
