Colon interposition for esophageal replacement: an alternative technique based on the use of the right colon
- PMID: 10674607
- PMCID: PMC1420983
- DOI: 10.1097/00000658-200002000-00004
Colon interposition for esophageal replacement: an alternative technique based on the use of the right colon
Abstract
Objective: To describe the technique and results of an alternative colon interposition procedure in which the ascending and transverse colon is used as graft, but that still relies on the left colonic artery for blood supply.
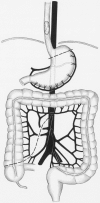
Summary background data: The standard procedure to obtain a left colon interposition graft requires ligation of the middle colic artery and mobilization of the left and right flexure. This approach carries a risk because preparation of the left flexure may damage arterial or venous collaterals located at this site that are crucial for graft perfusion.
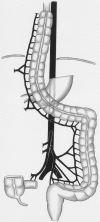
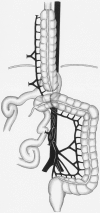
Methods: The authors modified the standard technique so that mobilization of the left flexure is no longer necessary. To obtain a colon interposition graft that is long enough, the ascending colon was included into the graft by ligating the middle and the right colic artery. The left colic artery remained the blood-supplying vessel. From January 1997 to June 1998, 15 patients underwent modified colon interposition with a cervical anastomosis (12 esophagectomies, 3 esophagogastrectomies).
Results: In all cases, intraoperative blood supply from the left colic artery to the proximal ascending colon was sufficient. After surgery, four major complications occurred (27%). Endoscopy demonstrated a vital graft in all patients. In one patient a leakage of the cervical anastomosis was observed. One patient died of herpes pneumonia. Postoperative artificial ventilation was required for an average of 2.8 +/- 4.6 days, the average intensive care unit stay was 6.9+/-4.5 days, and the average total hospital stay was 24.1 +/- 15.1 days.
Conclusion: An intact left colic artery, including its collaterals at the splenic flexure, supplies sufficient blood to the proximal ascending colon after central ligation of the middle and right colic artery. Even without mobilization of the left flexure, a sufficient graft length can be obtained. Preliminary complication rates with the use of this technique for colon interposition are in the range of those found for the standard colon interposition technique. These modifications may represent an alternative to established procedures for creating a colon interposition graft.
Figures
References
-
- Rice TW. Colon replacement. In: Pearson FG, Deslauriers J, Ginsberg RJ, et al, eds. Esophageal surgery. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1995: 761–774.
-
- Hiebert CA, Bredenberg CE. Selection and placement of conduits. In: Pearson FG, Deslauriers J, Ginsberg RJ, et al, eds. Esophageal surgery. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1995: 649–656.
-
- Sonneland J, Anson BJ, Beaton LE. Surgical anatomy of the arterial supply to the colon from the superior mesenteric artery based upon a study of 600 specimen. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1958; 106:385–398. - PubMed
-
- Kelling GE. Oesophagoplastik mit Hilfe des Querkolons. Zentralbl Chir 1911; 38:1209–1212.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

