Insulin resistance differentially affects the PI 3-kinase- and MAP kinase-mediated signaling in human muscle
- PMID: 10675357
- PMCID: PMC377440
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI7535
Insulin resistance differentially affects the PI 3-kinase- and MAP kinase-mediated signaling in human muscle
Abstract
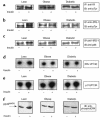
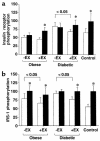
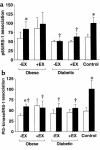
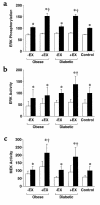
The broad nature of insulin resistant glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 diabetes suggests a defect in the proximal part of the insulin signaling network. We sought to identify the pathways compromised in insulin resistance and to test the effect of moderate exercise on whole-body and cellular insulin action. We conducted euglycemic clamps and muscle biopsies on type 2 diabetic patients, obese nondiabetics and lean controls, with and without a single bout of exercise. Insulin stimulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) pathway, as measured by phosphorylation of the insulin receptor and IRS-1 and by IRS protein association with p85 and with PI 3-kinase, was dramatically reduced in obese nondiabetics and virtually absent in type 2 diabetic patients. Insulin stimulation of the MAP kinase pathway was normal in obese and diabetic subjects. Insulin stimulation of glucose-disposal correlated with association of p85 with IRS-1. Exercise 24 hours before the euglycemic clamp increased phosphorylation of insulin receptor and IRS-1 in obese and diabetic subjects but did not increase glucose uptake or PI 3-kinase association with IRS-1 upon insulin stimulation. Thus, insulin resistance differentially affects the PI 3-kinase and MAP kinase signaling pathways, and insulin-stimulated IRS-1-association with PI 3-kinase defines a key step in insulin resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Kelley DE, Mokan M, Mandarino L. Intracellular defects in glucose metabolism in obese patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1992;41:698–706. - PubMed
-
- Bonadonna RC, et al. Roles of glucose transport and glucose phosphorylation in muscle insulin resistance of NIDDM. Diabetes. 1996;45:915–925. - PubMed
-
- Pendergrass M, et al. Insulin-induced hexokinase II expression is reduced in obesity and NIDDM. Diabetes. 1998;47:387–394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

