X-Linked syndrome of polyendocrinopathy, immune dysfunction, and diarrhea maps to Xp11.23-Xq13.3
- PMID: 10677306
- PMCID: PMC1288099
- DOI: 10.1086/302761
X-Linked syndrome of polyendocrinopathy, immune dysfunction, and diarrhea maps to Xp11.23-Xq13.3
Abstract
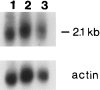
We describe genetic analysis of a large pedigree with an X-linked syndrome of polyendocrinopathy, immune dysfunction, and diarrhea (XPID), which frequently results in death during infancy or childhood. Linkage analysis mapped the XPID gene to a 17-cM interval defined by markers DXS8083 and DXS8107 on the X chromosome, at Xp11. 23-Xq13.3. The maximum LOD score was 3.99 (recombination fraction0) at DXS1235. Because this interval also harbors the gene for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS), we investigated mutations in the WASP gene, as the molecular basis of XPID. Northern blot analysis detected the same relative amount and the same-sized WASP message in patients with XPID and in a control. Analysis of the WASP coding sequence, an alternate promoter, and an untranslated upstream first exon was carried out, and no mutations were found in patients with XPID. A C-->T transition within the alternate translation start site cosegregated with the XPID phenotype in this family; however, the same transition site was detected in a normal control male. We conclude that XPID maps to Xp11.23-Xq13.3 and that mutations of WASP are not associated with XPID.
Figures



References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Fondation Jean Dausset/CEPH, http://www.cephb.fr/cephdb
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/GenbankOverview.html(for WASP alternate promoter and untranslated exon [accession number AF115548] and WASP exons 1 and 2 and intron 1 [accession number AF115549])
-
- GeneMap'99, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genemap/
-
- Généthon, http://www.genethon.fr
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://www.marshmed.org/genetics
References
-
- Colletti RB, Guillot AP, Rosen S, Bhan AK, Hobson CD, Collins AB, Russell GJ, et al (1991) Autoimmune enteropathy and nephropathy with circulating anti-epithelial cell antibodies. J Pediatr 118:858–864 - PubMed
-
- Derry JM, Ochs HD, Francke U (1994) Isolation of a novel gene mutated in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Cell 78:635–644 (erratum: Cell 79:923) - PubMed
-
- Derry JM, Wiedemann P, Blair P, Wang Y, Kerns JA, Lemahieu V, Godfrey VL, et al (1995) The mouse homolog of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) gene is highly conserved and maps near the scurfy (sf) mutation on the X chromosome. Genomics 29:471–477 - PubMed
-
- De Saint Basile G, Lagelouse RD, Lambert N, Schwarz K, Le Mareck B, Odent S, Schlegel N, et al (1996) Isolated X-linked thrombocytopenia in two unrelated families is associated with point mutations in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein gene. J Pediatr 129:56–62 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

