A unique form of mental retardation with a distinctive phenotype maps to Xq26-q27
- PMID: 10677307
- PMCID: PMC1288100
- DOI: 10.1086/302772
A unique form of mental retardation with a distinctive phenotype maps to Xq26-q27
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet 2000 Apr;66(4):1472
Abstract
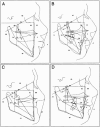
We report a novel X-linked mental retardation (XLMR) syndrome, with characteristic facial dysmorphic features, segregating in a large North Carolina family. Only males are affected, over four generations. Clinical findings in the seven living affected males include a moderate degree of mental retardation (MR), coarse facies, puffy eyelids, narrow palpebral fissures, prominent supraorbital ridges, a bulbous nose, a prominent lower lip, large ears, obesity, and large testicles. Cephalometric measurements suggest that the affected males have a distinctive craniofacial skeletal structure, when compared with normative measures. Obligate-carrier females are unaffected with MR, but the results of cephalometric skeletal analysis suggest craniofacial dysmorphisms intermediate between affected males and normative control individuals. Unaffected male relatives show no clinical or cephalometric resemblance to affected males. The blood-lymphocyte karyotype and the results of DNA analysis for fragile-X syndrome and of other routine investigations are normal. Linkage analysis for polymorphic DNA markers spanning the X chromosome established linkage to Xq26-q27. Maximum LOD scores were obtained at marker DXS1047 (maximum LOD score = 3.1 at recombination fraction 0). By use of haplotype analysis, we have localized the gene for this condition to an 18-cM genetic interval flanked by ATA59C05 and GATA31E08. On the basis of both the clinical phenotype and the mapping data, we were able to exclude other reported XLMR conditions. Therefore, we believe that a unique recessive XLMR syndrome with a distinctive and recognizable phenotype is represented in this family.
Figures




References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Cooperative Human Linkage Center, The http://www.chlc.org/ (for chromosome X integrated marker map, version v8c7)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for BFLS [MIM 301900], SGBS [MIM 312879], ATR-X [MIM 300032], and Lesch-Nyhan syndrome [MIM 308000])
References
-
- Atkin JF, Flaitz K, Patil S, Smith W (1985) A new X-linked mental retardation syndrome. Am J Med Genet 21:697–705 - PubMed
-
- Baraitser M, Reardon W, Vijeratnam S (1995) Nonspecific X-linked mental retardation with macrocephaly and obesity: a further family. Am J Med Genet 57:380–384 - PubMed
-
- Behmel A, Plochl E, Rosenkranz W (1988) A new X-linked dysplasia gigantism syndrome: follow-up in the first family and report on a second Austrian family. Am J Med Genet 30:275–285 - PubMed
-
- Bland JH (1968) Proceedings of seminars on the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Fed Proc 27:1017–1112
-
- Börjeson M, Forssman H, Lehmann O (1962) An X-linked recessively inherited syndrome characterized by grave mental deficiency, epilepsy and endocrine disorder. Acta Med Scand 171:13–21 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

