Allosteric inhibitors of inducible nitric oxide synthase dimerization discovered via combinatorial chemistry
- PMID: 10677491
- PMCID: PMC26464
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.4.1506
Allosteric inhibitors of inducible nitric oxide synthase dimerization discovered via combinatorial chemistry
Abstract
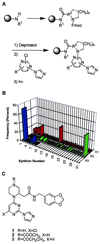
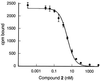
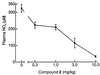
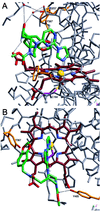
Potent and selective inhibitors of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) (EC ) were identified in an encoded combinatorial chemical library that blocked human iNOS dimerization, and thereby NO production. In a cell-based iNOS assay (A-172 astrocytoma cells) the inhibitors had low-nanomolar IC(50) values and thus were >1,000-fold more potent than the substrate-based direct iNOS inhibitors 1400W and N-methyl-l-arginine. Biochemical studies confirmed that inhibitors caused accumulation of iNOS monomers in mouse macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. High affinity (K(d) approximately 3 nM) of inhibitors for isolated iNOS monomers was confirmed by using a radioligand binding assay. Inhibitors were >1,000-fold selective for iNOS versus endothelial NOS dimerization in a cell-based assay. The crystal structure of inhibitor bound to the monomeric iNOS oxygenase domain revealed inhibitor-heme coordination and substantial perturbation of the substrate binding site and the dimerization interface, indicating that this small molecule acts by allosterically disrupting protein-protein interactions at the dimer interface. These results provide a mechanism-based approach to highly selective iNOS inhibition. Inhibitors were active in vivo, with ED(50) values of <2 mg/kg in a rat model of endotoxin-induced systemic iNOS induction. Thus, this class of dimerization inhibitors has broad therapeutic potential in iNOS-mediated pathologies.
Figures

References
-
- Griffith O W, Stuehr D J. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:707–736. - PubMed
-
- Marletta M A. Cell. 1994;78:927–930. - PubMed
-
- Masters B S, McMillan K, Sheta E A, Nishima J S, Roman L J, Martasek P. FASEB J. 1996;10:552–558. - PubMed
-
- Bredt D S, Hwang P M, Glatt C E, Lowenstein C, Reed R R, Snyder S H. Nature (London) 1991;351:714–718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

