Induction of topoisomerase I cleavage complexes by 1-beta -D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (ara-C) in vitro and in ara-C-treated cells
- PMID: 10677551
- PMCID: PMC26531
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.4.1885
Induction of topoisomerase I cleavage complexes by 1-beta -D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (ara-C) in vitro and in ara-C-treated cells
Abstract
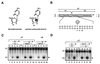
1-beta-d-Arabinofuranosylcytosine (Ara-C) is a nucleoside analog commonly used in the treatment of leukemias. Ara-C inhibits DNA polymerases and can be incorporated into DNA. Its mechanism of cytotoxicity is not fully understood. Using oligonucleotides and purified human topoisomerase I (top1), we found a 4- to 6-fold enhancement of top1 cleavage complexes when ara-C was incorporated at the +1 position (immediately 3') relative to a unique top1 cleavage site. This enhancement was primarily due to a reversible inhibition of top1-mediated DNA religation. Because ara-C incorporation is known to alter base stacking and sugar puckering at the misincorporation site and at the neighboring base pairs, the observed inhibition of religation at the ara-C site suggests the importance of the alignment of the 5'-hydroxyl end for religation with the phosphate group of the top1 phosphotyrosine bond. This study also demonstrates that ara-C treatment and DNA incorporation trap top1 cleavage complexes in human leukemia cells. Finally, we report that camptothecin-resistant mouse P388/CPT45 cells with no detectable top1 are crossresistant to ara-C, which suggests that top1 poisoning is a potential mechanism for ara-C cytotoxicity.
Figures




References
-
- Hsieh T, Lee M P, Brown S D. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;29:191–200. - PubMed
-
- Wang J C. Annu Rev Biochem. 1996;65:635–692. - PubMed
-
- Champoux J. In: Mechanistic Aspects of Type-I Topoisomerases. Wang J C, Cozarelli N R, editors. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1990. pp. 217–242.
-
- Gupta M, Fujimori A, Pommier Y. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1262:1–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

