Interferon consensus sequence binding protein confers resistance against Yersinia enterocolitica
- PMID: 10678954
- PMCID: PMC97295
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.3.1408-1417.2000
Interferon consensus sequence binding protein confers resistance against Yersinia enterocolitica
Abstract
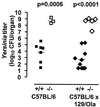
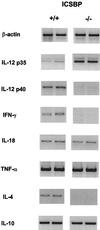
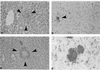
Interferon consensus sequence binding protein (ICSBP)-deficient mice display enhanced susceptibility to intracellular pathogens. At least two distinct immunoregulatory defects are responsible for this phenotype. First, diminished production of reactive oxygen intermediates in macrophages results in impaired intracellular killing of microorganisms. Second, defective early interleukin-12 (IL-12) production upon microbial challenge leads to a failure in gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) induction and subsequently in T helper 1 immune responses. Here, we investigated the role of ICSBP in resistance against the extracellular bacterium Yersinia enterocolitica. ICSBP(-/-) mice failed to produce IL-12 and IFN-gamma, but also IL-4, after Yersinia challenge. In addition, granuloma formation was highly disturbed in infected ICSBP(-/-) mice, leading to multiple necrotic abscesses in affected organs. Consequently, ICSBP(-/-) mice rapidly succumbed to acute Yersinia infection. In vitro treatment of spleen cells from ICSBP(-/-) mice with recombinant IL-12 (rIL-12) or rIL-18 in combination with a second stimulus resulted in IFN-gamma induction. In experimental therapy of infected ICSBP(-/-) mice, we observed that administration of rIL-12 induced IFN-gamma production which was associated with improved resistance to Yersinia. In contrast, treatment with rIL-18 failed to enhance endogenous IFN-gamma production but nevertheless reduced bacterial burden in ICSBP(-/-) mice. Although cytokine therapy with rIL-12 or rIL-18 ameliorated the course of Yersinia infection in ICSBP(-/-) mice, both cytokines failed to completely restore impaired immunity. Taken together, the results indicate that the transcription factor ICSBP is essential for efficient host immune defense against Yersinia. These results are important for understanding the complex host immune responses in bacterial infections.
Figures




Similar articles
-
IL-12 is essential for resistance against Yersinia enterocolitica by triggering IFN-gamma production in NK cells and CD4+ T cells.J Immunol. 1996 Feb 15;156(4):1458-68. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8568248
-
Interferon consensus sequence binding protein-deficient mice display impaired resistance to intracellular infection due to a primary defect in interleukin 12 p40 induction.J Exp Med. 1997 Nov 3;186(9):1523-34. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.9.1523. J Exp Med. 1997. PMID: 9348310 Free PMC article.
-
Ambiguous role of interleukin-12 in Yersinia enterocolitica infection in susceptible and resistant mouse strains.Infect Immun. 1998 May;66(5):2213-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.5.2213-2220.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9573110 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Yersinia enterocolitica infection in rodents: a model for human yersiniosis.APMIS. 1993 Jun;101(6):417-29. APMIS. 1993. PMID: 8363822 Review.
-
ICSBP/IRF-8: its regulatory roles in the development of myeloid cells.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002 Jan;22(1):145-52. doi: 10.1089/107999002753452755. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002. PMID: 11846985 Review.
Cited by
-
Yersinia enterocolitica in Crohn's disease.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Mar 8;13:1129996. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1129996. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36968108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Most Important Virulence Markers of Yersinia enterocolitica and Their Role during Infection.Genes (Basel). 2018 May 3;9(5):235. doi: 10.3390/genes9050235. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29751540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histamine signaling through the H(2) receptor in the Peyer's patch is important for controlling Yersinia enterocolitica infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 13;103(24):9268-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510414103. Epub 2006 May 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16717182 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of T helper cell differentiation by interferon regulatory factor family members.Immunol Res. 2012 Dec;54(1-3):169-76. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8328-0. Immunol Res. 2012. PMID: 22528124 Review.
-
Interferon regulatory factor 8 regulates pathways for antigen presentation in myeloid cells and during tuberculosis.PLoS Genet. 2011 Jun;7(6):e1002097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002097. Epub 2011 Jun 23. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21731497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Autenrieth I B, Firsching R. Penetration of M cells and destruction of Peyer's patches by Yersinia enterocolitica: an ultrastructural and histological study. J Med Microbiol. 1996;44:285–294. - PubMed
-
- Autenrieth I B, Heesemann J. In vivo neutralization of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma abrogates resistance to Yersinia enterocolitica infection in mice. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181:333–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

