The puc1 cyclin regulates the G1 phase of the fission yeast cell cycle in response to cell size
- PMID: 10679013
- PMCID: PMC14792
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.11.2.543
The puc1 cyclin regulates the G1 phase of the fission yeast cell cycle in response to cell size
Abstract
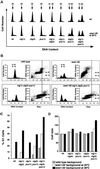
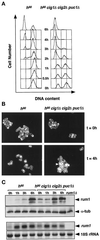
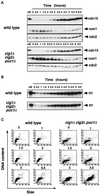
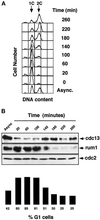
Eukaryotic cells coordinate cell size with cell division by regulating the length of the G1 and G2 phases of the cell cycle. In fission yeast, the length of the G1 phase depends on a precise balance between levels of positive (cig1, cig2, puc1, and cdc13 cyclins) and negative (rum1 and ste9-APC) regulators of cdc2. Early in G1, cyclin proteolysis and rum1 inhibition keep the cdc2/cyclin complexes inactive. At the end of G1, the balance is reversed and cdc2/cyclin activity down-regulates both rum1 and the cyclin-degrading activity of the APC. Here we present data showing that the puc1 cyclin, a close relative of the Cln cyclins in budding yeast, plays an important role in regulating the length of G1. Fission yeast cells lacking cig1 and cig2 have a cell cycle distribution similar to that of wild-type cells, with a short G1 and a long G2. However, when the puc1(+) gene is deleted in this genetic background, the length of G1 is extended and these cells undergo S phase with a greater cell size than wild-type cells. This G1 delay is completely abolished in cells lacking rum1. Cdc2/puc1 function may be important to down-regulate the rum1 Cdk inhibitor at the end of G1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A WD repeat protein controls the cell cycle and differentiation by negatively regulating Cdc2/B-type cyclin complexes.Mol Biol Cell. 1997 Dec;8(12):2475-86. doi: 10.1091/mbc.8.12.2475. Mol Biol Cell. 1997. PMID: 9398669 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclins of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Semin Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;6(2):73-8. doi: 10.1016/1043-4682(95)90003-9. Semin Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7548845 Review.
-
Regulation of G1 progression in fission yeast by the rum1+ gene product.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 1996;2:29-35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5873-6_3. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 1996. PMID: 9552380 Review.
-
B-type cyclins regulate G1 progression in fission yeast in opposition to the p25rum1 cdk inhibitor.EMBO J. 1996 Feb 15;15(4):839-49. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8631305 Free PMC article.
-
A single fission yeast mitotic cyclin B p34cdc2 kinase promotes both S-phase and mitosis in the absence of G1 cyclins.EMBO J. 1996 Feb 15;15(4):850-60. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8631306 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cyclin/Cdk complexes: their involvement in cell cycle progression and mitotic division.Protoplasma. 2001;216(3-4):119-42. doi: 10.1007/BF02673865. Protoplasma. 2001. PMID: 11732181 Review.
-
Size Does Matter: Why Polyploid Tumor Cells are Critical Drug Targets in the War on Cancer.Front Oncol. 2014 May 26;4:123. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00123. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24904834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of the RNA-binding protein Zfs1 modulates sexual differentiation in fission yeast.J Cell Sci. 2017 Dec 15;130(24):4144-4154. doi: 10.1242/jcs.208066. Epub 2017 Oct 30. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 29084823 Free PMC article.
-
Computational modeling of chromosome re-replication in mutant strains of fission yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Apr 19;32(9):830-841. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-09-0610. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33534609 Free PMC article.
-
APC(ste9/srw1) promotes degradation of mitotic cyclins in G(1) and is inhibited by cdc2 phosphorylation.EMBO J. 2000 Aug 1;19(15):3945-55. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.15.3945. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10921876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Booher RN, Alfa CE, Hyams JS, Beach D. The fission yeast cdc2/cdc13/suc1 protein kinase: regulation of catalytic activity and nuclear localization. Cell. 1989;58:485–497. - PubMed
-
- Bueno A, Richardson H, Reed SI, Russell P. A fission yeast B-type cyclin functioning early in the cell cycle. Cell. 1991;66:149–160. - PubMed
-
- Carlson CR, Grallert B, Stokke T, Boye E. Regulation of the start of DNA replication in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Cell Sci. 1999;112:939–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

