Identification and analysis of the K5 gene of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
- PMID: 10684303
- PMCID: PMC111777
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.6.2867-2875.2000
Identification and analysis of the K5 gene of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
Abstract
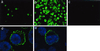
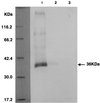
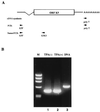
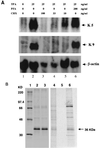
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), or human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), belongs to the gammaherpesvirus subfamily and encodes approximately 80 open reading frames (ORFs). Among them are a few candidates for immediate-early genes (e.g., K5). We developed a monoclonal antibody (MAb), 328C7, against the K5 antigen. This MAb reacted with the K5 gene product by immunoscreening of a cDNA library from BCBL-1 cells, and this result was confirmed by transfection of the K5 ORF into Cos-7 cells. After induction of lytic infection by treatment with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, MAb 328C7 reacted with an antigen in the cytoplasm of BCBL-1 and BC-3 cells as early as after 4 h of induction. Immunoelectron microscopy showed that the K5 antigen was situated mainly in the endoplasmic reticulum but was not present on the virion or in the nucleus. Northern blotting with a K5-specific probe revealed a single transcript of 1.2 kb, while Western blotting showed the antigen to be a 36-kDa polypeptide. The 5' and 3' ends were then determined by rapid amplification of cDNA, followed by sequencing of RACE products, and a splice was revealed upstream of the K5 ORF. K5 expression was unaffected by the respective DNA and protein synthesis inhibitors phosphonoformic acid and cycloheximide plus actinomycin D, confirming its immediate-early nature. Transient-transfection assays showed that the K5 promoter was transactivated by ORF 50 (KSHV Rta), a homolog of Epstein-Barr virus Rta, but the K5 gene product exhibited no transregulation of its own promoter or those of DNA polymerase and the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. This is the first such analysis of an immediate-early gene product; determination of its specific biological function requires further investigation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
ERK1/2 and MEK1/2 induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) early during infection of target cells are essential for expression of viral genes and for establishment of infection.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(16):10308-29. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10308-10329.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16051824 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of human herpesvirus 8 open reading frame K5 independent of ORF50 expression.Virus Res. 2002 Dec;90(1-2):77-89. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(02)00142-9. Virus Res. 2002. PMID: 12457964
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha is induced during the early stages of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic cycle reactivation and together with the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) cooperatively stimulates the viral RTA, MTA, and PAN promoters.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9590-612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9590-9612.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915572 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus viral interferon regulatory factor gene.J Virol. 2000 Sep;74(18):8623-34. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.18.8623-8634.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10954564 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of gene expression and a transactivation function exhibited by the vGCR (ORF74) chemokine receptor protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.J Virol. 2002 Apr;76(7):3421-39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.7.3421-3439.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11884567 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encodes two proteins that block cell surface display of MHC class I chains by enhancing their endocytosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jul 5;97(14):8051-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.140129797. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10859362 Free PMC article.
-
Split genes and their expression in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.Rev Med Virol. 2003 May-Jun;13(3):173-84. doi: 10.1002/rmv.387. Rev Med Virol. 2003. PMID: 12740832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification of binding sites for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic switch protein, RTA.Virology. 2009 Apr 10;386(2):290-302. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.01.031. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19233445 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic organization and hypoxic activation of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF34-37 gene cluster.J Virol. 2006 Jul;80(14):7037-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00553-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16809309 Free PMC article.
-
Negative elongation factor-mediated suppression of RNA polymerase II elongation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic gene expression.J Virol. 2012 Sep;86(18):9696-707. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01012-12. Epub 2012 Jun 27. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22740393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arvanitakis L, Mesri E A, Nador R G, Said J W, Asch A S, Knowles D M, Cesarman E. Establishment and characterization of a primary effusion (body cavity-based) lymphoma cell line (BC-3) harboring Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KHSV/HHV-8) in the absence of Epstein-Barr virus. Blood. 1996;88:2648–2654. - PubMed
-
- Bais C, Santomasso B, Coso O, Arvanitakis L, Raakar E G, Gutkind J S, Asch A S, Cesarmans E, Gerhengorn M C, Mesri E A. G-protein-coupled receptor of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is a viral oncogene and angiogenesis activator. Nature. 1998;391:86–89. - PubMed
-
- Boshoff C, Endo Y, Collins P D, Takeuchi Y, Reeves J D, Schweickart V L, Siani M A, Sasaki T, Williams T J, Gray P W, Moore P S, Chang Y, Weiss R A. Angiogenic and HIV-inhibitory functions of KSHV-encoded chemokines. Science. 1997;278:290–294. - PubMed
-
- Burger R, Neipel F, Fleckenstein B, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Kalden J R, Gramatzki M. Human herpesvirus type 8 interleukin-6 homologue is functionally active on human myeloma cells. Blood. 1998;91:1858–1863. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore P S, Said J W, Knowles D M. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1186–1191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

