Disassociation of met-mediated biological responses in vivo: the natural hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor splice variant NK2 antagonizes growth but facilitates metastasis
- PMID: 10688652
- PMCID: PMC110822
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.6.2055-2065.2000
Disassociation of met-mediated biological responses in vivo: the natural hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor splice variant NK2 antagonizes growth but facilitates metastasis
Abstract
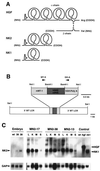
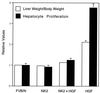
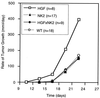
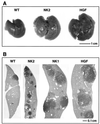
Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF) stimulates numerous cellular activities capable of contributing to the metastatic phenotype, including growth, motility, invasiveness, and morphogenetic transformation. When inappropriately expressed in vivo, an HGF/SF transgene induces numerous hyperplastic and neoplastic lesions. NK1 and NK2 are natural splice variants of HGF/SF; all interact with a common receptor, Met. Although both agonistic and antagonistic properties have been ascribed to each isoform in vitro, NK1 retains the full spectrum of HGF/SF-like activities when expressed as a transgene in vivo. Here we report that transgenic mice broadly expressing NK2 exhibit none of the phenotypes characteristic of HGF/SF or NK1 transgenic mice. Instead, when coexpressed in NK2-HGF/SF bitransgenic mice, NK2 antagonizes the pathological consequences of HGF/SF and discourages the subcutaneous growth of transplanted Met-containing melanoma cells. Remarkably, the metastatic efficiency of these same melanoma cells is dramatically enhanced in NK2 transgenic host mice relative to wild-type recipients, rivaling levels achieved in HGF/SF and NK1 transgenic hosts. Considered in conjunction with reports that in vitro NK2 induces scatter, but not other activities, these data strongly suggest that cellular motility is a critical determinant of metastasis. Moreover, our results demonstrate how alternatively structured ligands can be exploited in vivo to functionally dissociate Met-mediated activities and their downstream pathways.
Figures

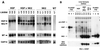


References
-
- Bardelli A, Basile M L, Audero E, Giordano S, Wennstrom S, Menard S, Comoglio P M, Ponzetto C. Concomitant activation of pathways downstream of Grb2 and PI 3-kinase is required for MET-mediated metastasis. Oncogene. 1999;18:1139–1146. - PubMed
-
- Bellusci S, Moens G, Gaudino G, Comoglio P, Nakamura T, Thiery J-P, Jouanneau J. Creation of a hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor autocrine loop in carcinoma cells induces invasive properties associated with increased tumorigenicity. Oncogene. 1994;9:1091–1099. - PubMed
-
- Bladt F, Riethmacher D, Isenmann S, Aguzzi A, Birchmeier C. Essential role for the c-met receptor in the migration of myogenic precursor cells into the limb bud. Nature. 1995;376:768–771. - PubMed
-
- Bottaro D P, Rubin J S, Faletto D L, Chan A M, Kmiecik T E, Vande Woude G F, Aaronson S A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991;251:802–804. - PubMed
-
- Castagnino P, Soriano J V, Montesano R, Bottaro D P. Induction of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 is a delayed early cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor. Oncogene. 1998;17:481–492. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
