Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 requires prior dissociation of the ASK1 inhibitor thioredoxin
- PMID: 10688666
- PMCID: PMC110836
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.6.2198-2208.2000
Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 requires prior dissociation of the ASK1 inhibitor thioredoxin
Abstract
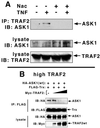
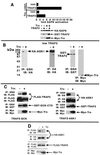
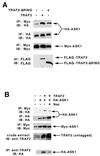
The stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs, also called c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinases) and the p38s, two mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) subgroups activated by cytokines of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family, are pivotal to the de novo gene expression elicited as part of the inflammatory response. Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) is a MAPK kinase kinase (MAP3K) that activates both the SAPKs and p38s in vivo. Here we show that TNF receptor (TNFR) associated factor 2 (TRAF2), an adapter protein that couples TNFRs to the SAPKs and p38s, can activate ASK1 in vivo and can interact in vivo with the amino- and carboxyl-terminal noncatalytic domains of the ASK1 polypeptide. Expression of the amino-terminal noncatalytic domain of ASK1 can inhibit TNF and TRAF2 activation of SAPK. TNF can stimulate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and the redox-sensing enzyme thioredoxin (Trx) is an endogenous inhibitor of ASK1. We also show that expression of TRAF2 fosters the production of ROS in transfected cells. We demonstrate that Trx significantly inhibits TRAF2 activation of SAPK and blocks the ASK1-TRAF2 interaction in a reaction reversed by oxidants. Finally, the mechanism of ASK1 activation involves, in part, homo-oligomerization. We show that expression of ASK1 with TRAF2 enhances in vivo ASK1 homo-oligomerization in a manner dependent, in part, upon the TRAF2 RING effector domain and the generation of ROS. Thus, activation of ASK1 by TNF requires the ROS-mediated dissociation of Trx possibly followed by the binding of TRAF2 and consequent ASK1 homo-oligomerization.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced germinal center kinase-related (GCKR) and stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) activation depends upon the E2/E3 complex Ubc13-Uev1A/TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2).J Biol Chem. 2003 Apr 25;278(17):15429-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211796200. Epub 2003 Feb 18. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12591926
-
Tumor necrosis factor signaling to stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK)/Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38. Germinal center kinase couples TRAF2 to mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase kinase 1 and SAPK while receptor interacting protein associates with a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase upstream of MKK6 and p38.J Biol Chem. 1998 Aug 28;273(35):22681-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.35.22681. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9712898
-
ASK1 is essential for JNK/SAPK activation by TRAF2.Mol Cell. 1998 Sep;2(3):389-95. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80283-x. Mol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9774977
-
Physiological roles of ASK1-mediated signal transduction in oxidative stress- and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis: advanced findings from ASK1 knockout mice.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002 Jun;4(3):415-25. doi: 10.1089/15230860260196218. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002. PMID: 12215209 Review.
-
Redox control of cell death.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002 Jun;4(3):405-14. doi: 10.1089/15230860260196209. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002. PMID: 12215208 Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 mediates MPTP toxicity and regulates glial activation.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29935. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029935. Epub 2012 Jan 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22253830 Free PMC article.
-
Self-incompatibility in the Brassicaceae: receptor-ligand signaling and cell-to-cell communication.Plant Cell. 2002;14 Suppl(Suppl):S227-38. doi: 10.1105/tpc.010440. Plant Cell. 2002. PMID: 12045279 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Use and abuse of exogenous H2O2 in studies of signal transduction.Free Radic Biol Med. 2007 Apr 1;42(7):926-32. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.01.011. Epub 2007 Jan 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007. PMID: 17349920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 control reactive oxygen species release, mitochondrial autophagy, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase/p38 phosphorylation during necrotizing enterocolitis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2009 Nov-Dec;2(5):297-306. doi: 10.4161/oxim.2.5.9541. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2009. PMID: 20716917 Free PMC article.
-
Novel strategy for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: enhancement of apoptosis.Lung. 2010 Jun;188(3):179-89. doi: 10.1007/s00408-010-9233-8. Epub 2010 Mar 6. Lung. 2010. PMID: 20213196 Review.
References
-
- Arch R H, Gedrich R W, Thompson C B. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs)—a family of adapter proteins that regulates life and death. Genes Dev. 1998;12:2821–2830. - PubMed
-
- Brenner D A, O'Hara M, Angel P, Chojkier M, Karin M. Prolonged activation of c-jun and collagenase genes by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989;337:661–663. - PubMed
-
- Chang H Y, Nishitoh H, Yang X, Ichijo H, Baltimore D. Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) by the adapter protein Daxx. Science. 1998;281:1860–1863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
