CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides enhance T-cell receptor-triggered interferon-gamma production and up-regulation of CD69 via induction of antigen-presenting cell-derived interferon type I and interleukin-12
- PMID: 10692033
- PMCID: PMC2327140
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00964.x
CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides enhance T-cell receptor-triggered interferon-gamma production and up-regulation of CD69 via induction of antigen-presenting cell-derived interferon type I and interleukin-12
Abstract
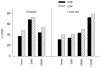
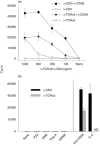
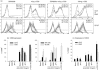
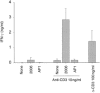
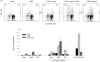
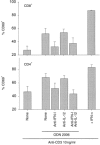
Bacterial cytidine-phosphate-guanosine (CpG-DNA) activates antigen-presenting cells (APC) and drives T helper 1 (Th1)-polarized immune responses in the mouse. Claims have been made that CpG-DNA costimulates murine T cells. We examined the direct and indirect effects of CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG-ODN) on human T-cell activation. CpG-ODN failed to costimulate purified human T cells activated with alpha-CD3 or alpha-T-cell receptor (TCR)alphabeta antibodies. In contrast, CpG-ODN sequence-specifically caused increased expression of CD69 on CD4 and CD8 T cells when peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were stimulated via alpha-CD3. CpG-ODN and alpha-CD3 stimulation synergized to induce interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, as shown by intracellular fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) staining. These effects of CpG-ODN on human T cells were caused by the release of IFN type I (IFN-I) and interleukin-12 (IL-12) from PBMC. Enhancement of CD69 expression on alpha-CD3-triggered T cells could be reproduced in a coculture transwell system of purified T cells and PBMC, was inhibited by neutralizing antibodies to IFN-I and could be mimicked by adding exogenous IFN-I. Furthermore, neutralization of either IFN-I or IL-12 diminished, and in combination abolished, IFN-gamma production. These findings show that CpG-ODN potentiate TCR-triggered activation of human T cells in an APC-dependent manner.
Figures


References
-
- Krieg AM, Yi AK, Matson S, et al. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA trigger direct B-cell activation. Nature. 1995;374:546. - PubMed
-
- Yi AK, Krieg AM. Rapid induction of mitogen-activated protein kinases by immune stimulatory CpG DNA. J Immunol. 1998;161:4493. - PubMed
-
- Stacey KJ, Sweet MJ, Hume DA. Macrophages ingest and are activated by bacterial DNA. J Immunol. 1996;157:2116. - PubMed
-
- Lipford GB, Sparwasser T, Bauer M, et al. Immunostimulatory DNA: sequence-dependent production of potentially harmful or useful cytokines. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:3420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

