Inhibition of immunoglobulin E response to Japanese cedar pollen allergen (Cry j 1) in mice by DNA immunization: different outcomes dependent on the plasmid DNA inoculation method
- PMID: 10692034
- PMCID: PMC2327145
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00935.x
Inhibition of immunoglobulin E response to Japanese cedar pollen allergen (Cry j 1) in mice by DNA immunization: different outcomes dependent on the plasmid DNA inoculation method
Abstract
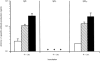
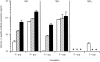
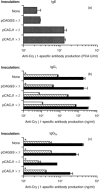
To develop a new immunotherapy for Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica; CJ) pollinosis, we evaluated the use of DNA immunization by inoculating mice with plasmid DNA encoding Cry j 1 as a CJ pollen major allergen (pCACJ1). Repeated intramuscular (i.m.) inoculation of BALB/c mice with pCACJ1 produced anti-Cry j 1 antibody responses, which were predominately of the immunoglobulin G2a (IgG2a) type. Furthermore, this inoculation suppressed immunoglobulin E (IgE) and IgG1 antibody responses to subsequent alum-precipitated Cry j 1 injections. Splenic T cells isolated from mice inoculated with pCACJ1 i.m. secreted interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), but not interleukin (IL)-4, in vitro upon stimulation with Cry j 1 as well as with p277-288, a peptide corresponding to the T-cell epitope of Cry j 1. In contrast, inoculation of BALB/c mice with pCACJ1 by gene gun injection caused response predominantly of the IgG1 type, and enhanced production of anti-Cry j 1 IgE antibodies to subsequent alum-precipitated Cry j 1 injections. Splenic T cells isolated from pCACJ1-innoculated mice by gene gun injection secreted both IFN-gamma and IL-4 in vitro, upon stimulation with Cry j 1 as well as with p277-288. These findings suggest that i.m. inoculation with pCACJ1 effectively elicits Cry j 1-specific T helper 1 (Th1)-type immune responses, resulting in inhibition of the IgE response to Cry j 1.
Figures


References
-
- Yasueda H, Yui Y, Shimizu T, Shida T. Isolation and partial characterization of the major allergen from Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) pollen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983;71:77. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi M, Inouye S, Taniai M, et al. Identification of the second major allergen of Japanese cedar pollen. Allergy. 1990;45:309. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto M, Nigi H, Sakaguchi M, et al. Sensitivity to two major allergens (Cry j I and Cry j II) in patients with Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) pollinosis. Clin Exp Allergy. 1995;25:848. - PubMed
-
- Sugimura K, Hashiguchi S, Takahashi Y, et al. Th1/Th2 response profiles to the major allergens Cry j 1 and Cry j 2 of Japanese cedar pollen. Allergy. 1996;51:732. - PubMed
-
- Taniai M, Ando S, Usui M, et al. N-terminal amino acid sequence of a major allergen of Japanese cedar pollen (Cry j I) FEBS Lett. 1988;239:329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

