Vibrio cholerae VibF is required for vibriobactin synthesis and is a member of the family of nonribosomal peptide synthetases
- PMID: 10692380
- PMCID: PMC94472
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.6.1731-1738.2000
Vibrio cholerae VibF is required for vibriobactin synthesis and is a member of the family of nonribosomal peptide synthetases
Abstract
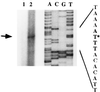
A 7.5-kbp fragment of chromosomal DNA downstream of the Vibrio cholerae vibriobactin outer membrane receptor, viuA, and the vibriobactin utilization gene, viuB, was recovered from a Sau3A lambda library of O395 chromosomal DNA. By analogy with the genetic organization of the Escherichia coli enterobactin gene cluster, in which the enterobactin biosynthetic and transport genes lie adjacent to the enterobactin outer membrane receptor, fepA, and the utilization gene, fes, the cloned DNA was examined for the ability to restore siderophore synthesis to E. coli ent mutants. Cross-feeding studies demonstrated that an E. coli entF mutant complemented with the cloned DNA regained the ability to synthesize enterobactin and to grow in low-iron medium. Sequence analysis of the cloned chromosomal DNA revealed an open reading frame downstream of viuB which encoded a deduced protein of greater than 2,158 amino acids, homologous to Yersinia sp. HMWP2, Vibrio anguillarum AngR, and E. coli EntF. A mutant with an in-frame deletion of this gene, named vibF, was created with classical V. cholerae strain O395 by in vivo marker exchange. In cross-feeding studies, this mutant was unable to synthesize ferric vibriobactin but was able to utilize exogenous siderophore. Complementation of the mutant with a cloned vibF fragment restored vibriobactin synthesis to normal. The expression of the vibF promoter was found to be negatively regulated by iron at the transcriptional level, under the control of the V. cholerae fur gene. Expression of vibF was not autoregulatory and neither affected nor was affected by the expression of irgA or viuA. The promoter of vibF was located by primer extension and was found to contain a dyad symmetric nucleotide sequence highly homologous to the E. coli Fur binding consensus sequence. A footprint of purified V. cholerae Fur on the vibF promoter, overlapping the Fur binding consensus sequence, was observed using DNase I footprinting. The protein product of vibF is homologous to the multifunctional nonribosomal protein synthetases and is necessary for the biosynthesis of vibriobactin.
Figures



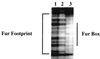
References
-
- Altschul A F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Blomfield I C, Vaughn V, Rest R F, Eisenstein B I. Allelic exchange in Escherichia coli using the Bacillus subtilis sacB gene and a temperature-sensitive pSC101 replicon. Mol Microbiol. 1991;5:1447–1457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

