Sustained ethanol inhibition of native AMPA receptors on medial septum/diagonal band (MS/DB) neurons
- PMID: 10694206
- PMCID: PMC1621129
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703039
Sustained ethanol inhibition of native AMPA receptors on medial septum/diagonal band (MS/DB) neurons
Abstract
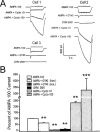
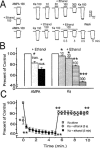
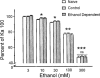
The direct impact of ethanol on native, non-NMDA glutamate receptors was examined in acutely isolated MS/DB neurons from rat. The impact of ethanol functional tolerance and physical dependence on non-NMDA receptor function was also determined. Non-NMDA receptors were defined pharmacologically as predominantly the AMPA subtype, because both AMPA- or kainate-activated currents were blocked by GYKI 52466, a selective AMPA receptor antagonist. The relative magnitude of potentiation of AMPA-activated currents by 10 or 100 microM cyclothiazide was consistent with recombinant AMPA flop-subtype receptors. Finally, the selective kainate receptor agonist, SYM 8021, induced little current in MS/DB neurons. AMPA receptor currents when activated by kainate were sensitive to ethanol, showing inhibition of approximately 5 - 50% when 10 - 300 mM ethanol and kainate were briefly co-applied (3 s). Ethanol (100 mM) also inhibited both the initial transient peak and sustained currents activated by AMPA. Inhibition was sustained during continuous ethanol superfusions of 5 min, suggesting a lack of acute tolerance to ethanol-induced AMPA receptor blockade. Rapid application of 3 - 3000 microM kainate activated concentration-dependent currents in MS/DB neurons from Control and Ethanol Dependent animals that were not significantly different. Also, direct ethanol inhibition (300 mM) of kainate-activated currents was not reduced by ethanol dependence, suggesting a lack of functional tolerance. These results suggest that native AMPA receptors on MS/DB neurons are inhibited by pharmacologically-relevant concentrations of ethanol. However, these receptors, unlike NMDA receptors, do not undergo adaptation with sustained ethanol exposure sufficient to induce physical dependence. British Journal of Pharmacology (2000) 129, 87 - 94
Figures

Similar articles
-
AMPA receptors on developing medial septum/diagonal band neurons are sensitive to early postnatal binge-like ethanol exposure.Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2003 Apr 14;142(1):89-99. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(03)00034-8. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12694947
-
Acute effects of ethanol on kainate receptors in cultured hippocampal neurons.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000 Feb;24(2):220-5. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000. PMID: 10698375
-
Ca2+-permeable non-NMDA glutamate receptors in rat magnocellular basal forebrain neurones.J Physiol. 1998 Apr 15;508 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):453-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.453bq.x. J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9508809 Free PMC article.
-
New developments in the molecular pharmacology of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate and kainate receptors.Pharmacol Ther. 1996;70(1):65-89. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(96)00014-9. Pharmacol Ther. 1996. PMID: 8804111 Review.
-
Kainate receptor agonists, antagonists and allosteric modulators.Curr Pharm Des. 2002;8(10):873-85. doi: 10.2174/1381612024607108. Curr Pharm Des. 2002. PMID: 11945137 Review.
Cited by
-
Respiratory depression in rats induced by alcohol and barbiturate and rescue by ampakine CX717.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012 Oct;113(7):1004-11. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00752.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 26. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012. PMID: 22837171 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol Induces Microglial Cell Death via the NOX/ROS/PARP/TRPM2 Signalling Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Dec 9;9(12):1253. doi: 10.3390/antiox9121253. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33317056 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate plasticity in the drunken amygdala: the making of an anxious synapse.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2010;91:205-33. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(10)91007-6. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20813244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synaptic effects induced by alcohol.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2013;13:31-86. doi: 10.1007/7854_2011_143. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 21786203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of positive AMPA modulators and their relationship to AMPA receptor subunits. A review of preclinical data.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Apr;179(1):154-63. doi: 10.1007/s00213-004-2065-6. Epub 2005 Jan 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15672275 Review.
References
-
- BHAVE S.V., SNELL L.D., TABAKOFF B., HOFFMAN P.L. Ethanol sensitivity of NMDA receptor function in developing cerebellar granule neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999;369:247–259. - PubMed
-
- CHANDLER L.J., NORWOOD D., SUTTON G. Chronic ethanol upregulates NMDA and AMPA, but not kainate receptor subunit proteins in rat primary cortical cultures. Alc. Clin. Exp. Res. 1999;23:363–370. - PubMed
-
- CHEN X.Y., MICHAELIS M.L., MICHAELIS E.K. Effects of chronic ethanol treatment on the expression of calcium transport carriers and NMDA/glutamate receptor proteins in brain synaptic membranes. J. Neurochem. 1997;69:1559–1569. - PubMed
-
- DILDY-MAYFIELD J.E., HARRIS R.A. Comparison of ethanol sensitivity of rat brain kainate, D,L-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxalone proprionic acid and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1992;262:487–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

