A novel anionic conductance affects action potential duration in isolated rat ventricular myocytes
- PMID: 10694227
- PMCID: PMC1571850
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703074
A novel anionic conductance affects action potential duration in isolated rat ventricular myocytes
Abstract
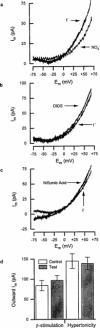
Effects of extracellular anions were studied in electrophysiological experiments on freshly isolated rat ventricular myocytes. Under current-clamp, action potential duration (APD) was prolonged by reducing the extracellular Cl(-) concentration and shortened by replacement of extracellular Cl(-) with I(-). Under voltage-clamp, membrane potential steps or ramps evoked an anionic background current (I(AB)) carried by either Cl(-), Br(-), I(-) or NO(3)(-). Activation of I(AB) was Ca(2+)- and cyclic AMP-independent, and was unaffected by cell shrinkage. I(AB) was insensitive to stilbene and fenamate anion transport blockers at concentrations that inhibit Ca(2+)-, cyclic AMP- and swelling-activated Cl(-) currents in ventricular cells of other mammals. These results suggest that I(AB) may be carried by a novel class of Cl(-) channel. Correlation of anion substitution experiments on membrane current and action potentials revealed that I(AB) could play a major role in controlling rat ventricular APD. These findings have important implications for those studying cardiac Cl(-) channels as potential targets for novel antiarrythmic agents.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unitary Cl- channels activated by cytoplasmic Ca2+ in canine ventricular myocytes.Circ Res. 1996 May;78(5):936-44. doi: 10.1161/01.res.78.5.936. Circ Res. 1996. PMID: 8620614
-
Swelling-activated and isoprenaline-activated chloride currents in guinea pig cardiac myocytes have distinct electrophysiology and pharmacology.J Gen Physiol. 1994 Dec;104(6):997-1017. doi: 10.1085/jgp.104.6.997. J Gen Physiol. 1994. PMID: 7699368 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of a calcium-activated chloride current in mouse ventricular myocytes.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002 Jul;283(1):H302-14. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00044.2002. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12063303
-
Role of cardiac chloride currents in changes in action potential characteristics and arrhythmias.Cardiovasc Res. 1998 Oct;40(1):23-33. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(98)00173-4. Cardiovasc Res. 1998. PMID: 9876314 Review.
-
Swelling-activated chloride channels in cardiac physiology and pathophysiology.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2003 May-Jul;82(1-3):25-42. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6107(03)00003-8. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12732266 Review.
Cited by
-
Nickel inhibits β-1 adrenoceptor mediated activation of cardiac CFTR chloride channels.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Mar 1;432(1):46-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.087. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23376720 Free PMC article.
-
A mathematical model of action potential heterogeneity in adult rat left ventricular myocytes.Biophys J. 2001 Dec;81(6):3029-51. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)75943-7. Biophys J. 2001. PMID: 11720973 Free PMC article.
-
An outwardly rectifying anionic background current in atrial myocytes from the human heart.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Aug 3;359(3):765-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.177. Epub 2007 Jun 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17560943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACKERMAN M.J., CLAPHAM D.E. Cardiac Cl− channels. Trends. Cardiovasc. Med. 1993;3:23–28. - PubMed
-
- BAHINKSY A., NAIRN A.C., GREENGARD P., GADSBY D.C. Chloride conductance regulated by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in cardiac myocytes. Nature. 1989;340:718–721. - PubMed
-
- BERUL C.I., SWEETEN T., VETTER V.L., MORAD M. Lack of cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator-type Cl− current in pediatric human atrial myocytes. Life Sci. 1997;60:189–197. - PubMed
-
- DU X., SOROTA S. Cardiac swelling-induced Cl− current depolarizes canine atrial myocytes. Am. J. Phys. 1997;272:H1904–H1916. - PubMed
-
- FAIVRE J., BRIL A. The cardiac Cl− channels as molecular targets for antiarrhythmic therapy. Fr. Pharm. Rev. Comm. 1997;9:61–70.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

