Apolipoprotein E isoform-dependent amyloid deposition and neuritic degeneration in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 10694577
- PMCID: PMC16026
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.050004797
Apolipoprotein E isoform-dependent amyloid deposition and neuritic degeneration in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
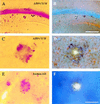
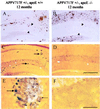
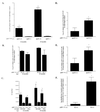
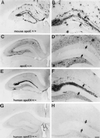
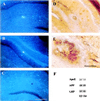
Apolipoprotein E (apoE) alleles determine the age-adjusted relative risk (epsilon4 > epsilon3) for Alzheimer's disease (AD). ApoE may affect AD pathogenesis by promoting deposition of the amyloid-beta (Abeta) peptide and its conversion to a fibrillar form. To determine the effect of apoE on Abeta deposition and AD pathology, we compared APP(V717F) transgenic (TG) mice expressing mouse, human, or no apoE (apoE(-/-)). A severe, plaque-associated neuritic dystrophy developed in APP(V717F) TG mice expressing mouse or human apoE. Though significant levels of Abeta deposition also occurred in APP(V717F) TG, apoE(-/-) mice, neuritic degeneration was virtually absent. Expression of apoE3 and apoE4 in APP(V717F) TG, apoE(-/-) mice resulted in fibrillar Abeta deposits and neuritic plaques by 15 months of age and substantially (>10-fold) more fibrillar deposits were observed in apoE4-expressing APP(V717F) TG mice. Our data demonstrate a critical and isoform-specific role for apoE in neuritic plaque formation, a pathological hallmark of AD.
Figures
References
-
- Selkoe D J. Science. 1997;275:630–631. - PubMed
-
- Lansbury P T J. Neuron. 1997;19:1151–1154. - PubMed
-
- Games D, Adams D, Alessandrini R, Barbour R, Berthelette P, Blackwell C, Carr T, Clemens J, Donaldson T, Gillespie F, et al. Nature (London) 1995;373:523–527. - PubMed
-
- Hsiao K, Chapman P, Nilsen S, Eckman C, Harigaya Y, Youkin S, Yang F, Cole G. Science. 1996;274:99–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

