Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR angiography and MR imaging of the carotid artery: high-resolution sequences in different acquisition planes
- PMID: 10696027
- PMCID: PMC7975334
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR angiography and MR imaging of the carotid artery: high-resolution sequences in different acquisition planes
Abstract
Background and purpose: First-pass contrast-enhanced MR angiography has become the technique of choice for studying the carotid bifurcation, but this method has some limitations. We evaluated the clinical utility of performing 3D contrast-enhanced MR angiography in the axial plane immediately after performing angiography in the coronal plane.
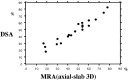
Methods: Cervical carotid arteries of 80 consecutive patients were studied on a 1.5-T MR imager with phased-array coils. Coronal 3D MR angiography was performed after administering a bolus injection of contrast material (20 mL) with automatic triggering. This was immediately followed by an axial acquisition. We measured carotid diameters on the contrast-enhanced MR angiograms as well as on intra-arterial digital subtraction angiograms according to established criteria. We also evaluated original source MR angiograms.
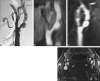
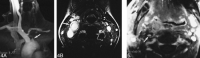
Results: Angiograms obtained in the axial plane correlated better with the intra-arterial digital subtraction angiograms than did the coronal angiograms. When first-pass contrast-enhanced MR angiography was incomplete because of a failure of triggering, the second-phase acquisition provided sufficient image quality. Original source images suffered from ring artifacts, low axial resolution, and a low level of soft-tissue visualization. Axial-based source images showed flow-independent contrast filling to the patent lumen with sufficient visualization of plaque morphology, thickened arterial wall, and surrounding disease processes, such as tumors.
Conclusion: With the addition of a 1-minute second-phase 3D acquisition in a different plane immediately after first-pass contrast-enhanced MR angiography, one can obtain a more accurate depiction of the carotid bifurcation, insurance against failure of triggering, and diagnostic source images.
Figures

References
-
- North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med 1991;325:445-453 - PubMed
-
- Executive Committee for the Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study Endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. JAMA 1995;273:1421-1428 - PubMed
-
- European Carotid Surgery Trialists' Collaborative Group MRC European Carotid Surgery Trial: interim results for symptomatic patients with severe (70–99%) or with mild (0–29%) carotid stenosis. Lancet 1991;337:1235-1243 - PubMed
-
- European Carotid Surgery Trialists' Collaborative Group Endarterectomy for moderate symptomatic carotid stenosis: interim results from the MRC European Carotid Surgery Trial. Lancet 1996;347:1591-1593 - PubMed
-
- Chaturvedi S, Policherla PN, Femino L. Cerebral angiography practices at US teaching hospitals: implications for carotid endarterectomy. Stroke 1997;28:1895-1897 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
