Dexamethasone attenuates the depressor response induced by neuropeptide Y microinjected into the nucleus tractus solitarius in rats
- PMID: 10696083
- PMCID: PMC1571908
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703122
Dexamethasone attenuates the depressor response induced by neuropeptide Y microinjected into the nucleus tractus solitarius in rats
Abstract
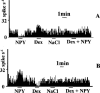
An investigation was made of the effect of dexamethasone (Dex) injection into the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) on the cardiovascular response to neuropeptide Y in rats. Dex (39 pmol) injected into the NTS inhibited the hypotension and bradycardia caused by NPY (5 pmol) with a short latency (10 min) and a long duration of action (up to 4 h). The rapid inhibition by Dex (39 pmol) of the cardiovascular response to NPY was not blocked by pretreatment with the glucocorticoid receptor blocker, RU38486 (47 or 117 pmol respectively), but was reversed by bicuculline (30 pmol). Microiontophoresis of NPY (0.01 mM, pH 6.5) into the NTS increased the spontaneous firing of the majority (68.4%) of baroreflex-excited cells, but decreased the firing of most (73.7%) baroreflex-inhibited cells. In contrast, Dex (0.02 M, pH 6.5) decreased the spontaneous firing of the majority of baroreflex-excited cells (42.1% of normal response) and decreased the inhibition of baroreflex-inhibited cells (47.5% of normal response). The responses of the majority of baroreceptive cells to NPY were blocked by iontophoretic administration of Dex. Dex (200 microM) increased the delayed rectifier outward K+ current by 31.4+/-1.1% (n=5), whereas NPY alone, at a concentration of 1.5 microM, inhibited the current by 28.6+/-0.8% (n=5). In the presence of Dex (200 microM), addition of NPY (1.5 microM) had no effect on the current. In conclusion, NTS-administered-Dex attenuated the cardiovascular response to NPY injected into the same area via a rapid membrane effect, which was mediated by an action on GABA(A) receptors and on the delayed rectifier outward K(+) channel.
Figures




References
-
- AGARWAL M.K., HAINQUE R., MOUSTAID N., LAZER G. Glucocorticoid antagonists. FEBS Lett. 1987;217:221–225. - PubMed
-
- ANDRESEN M.C., KUNZE D.L. Nucleus tractus solitarius gateway to neural circulatory control. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 1994;56:93–116. - PubMed
-
- BARRON K.W., PAVELKA S.M., GARRETT K.M. Diazepan-sensitive GABAA receptors in the NTS participate in cardiovascular control. Brain Res. 1997;773:53–60. - PubMed
-
- CHEN Y.Z., FU H., GUO Z.Membrane receptor for glucocorticoids in mammalian Neurons Methods in Neurosciences 199311Academic Press, San Diego; 16–28.Conn, M. (ed)
-
- DE JONG W. Noradrenaline: central inhibitory control of blood pressure and heart rate. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1974;29:179–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

