Pharmacological characterization of human recombinant melatonin mt(1) and MT(2) receptors
- PMID: 10696085
- PMCID: PMC1571913
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703130
Pharmacological characterization of human recombinant melatonin mt(1) and MT(2) receptors
Abstract
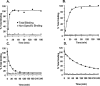
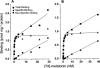
We have pharmacologically characterized recombinant human mt(1) and MT(2) receptors, stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO-mt(1) and CHO-MT(2)), by measurement of [(3)H]-melatonin binding and forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP (cAMP) production. [3H]-melatonin bound to mt(1) and MT(2) receptors with pK(D) values of 9.89 and 9.56 and B(max) values of 1.20 and 0.82 pmol mg(-1) protein, respectively. Whilst most melatonin receptor agonists had similar affinities for mt(1) and MT(2) receptors, a number of putative antagonists had substantially higher affinities for MT(2) receptors, including luzindole (11 fold), GR128107 (23 fold) and 4-P-PDOT (61 fold). In both CHO-mt(1) and CHO-MT(2) cells, melatonin inhibited forskolin-stimulated accumulation of cyclic AMP in a concentration-dependent manner (pIC(50) 9.53 and 9.74, respectively) causing 83 and 64% inhibition of cyclic AMP production at 100 nM, respectively. The potencies of a range of melatonin receptor agonists were determined. At MT(2) receptors, melatonin, 2-iodomelatonin and 6-chloromelatonin were essentially equipotent, whilst at the mt(1) receptor these agonists gave the rank order of potency of 2-iodomelatonin>melatonin>6-chloromelatonin. In both CHO-mt(1) and CHO-MT(2) cells, melatonin-induced inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP production was antagonized in a concentration-dependent manner by the melatonin receptor antagonist luzindole, with pA(2) values of 5.75 and 7.64, respectively. Melatonin-mediated responses were abolished by pre-treatment of cells with pertussis toxin, consistent with activation of G(i)/G(o) G-proteins. This is the first report of the use of [(3)H]-melatonin for the characterization of recombinant mt(1) and MT(2) receptors. Our results demonstrate that these receptor subtypes have distinct pharmacological profiles.
Figures




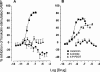
References
-
- ARENDT J. 1995London: Chapman and Hall; Melatonin and the mammalian pineal gland
-
- BERESFORD I.J.M., BROWNING C., STARKEY S.J., BROWN J., FOORD S.M., COUGHLAN J., NORTH P.C., DUBOCOVICH M.L., HAGAN R.M. GR196429: A non-indolic agonist at high-affinity melatonn receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap. 1998a;285:1239–1245. - PubMed
-
- BERESFORD I.J.M, , HARVEY F.J., HALL D.A., GILES H. Pharmacological characterisation of melatonin mt1 receptor mediated stimulation of [35S]-GTPγS binding. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998b;56:1167–1174. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

