Pharmacological characterization of small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels stably expressed in HEK 293 cells
- PMID: 10696100
- PMCID: PMC1571906
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703120
Pharmacological characterization of small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels stably expressed in HEK 293 cells
Abstract
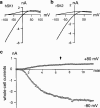
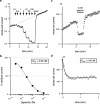
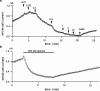
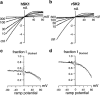
Three genes encode the small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels (SK channels). We have stably expressed hSK1 and rSK2 in HEK 293 cells and addressed the pharmacology of these subtypes using whole-cell patch clamp recordings. The bee venom peptide apamin blocked hSK1 as well as rSK2 with IC(50) values of 3.3 nM and 83 pM, respectively. The pharmacological separation between the subtypes was even more prominent when applying the scorpion peptide blocker scyllatoxin, which blocked hSK1 with an IC(50) value of 80 nM and rSK2 at 287 pM. The potent small molecule blockers showed little differentiation between the channel subtypes. The bis-quinolinium cyclophane UCL 1684 blocked hSK1 with an IC(50) value of 762 pM and rSK2 at 364 pM. The antiseptic compound dequalinium chloride blocked hSK1 and rSK2 with IC(50) values of 444 nM and 162 nM, respectively. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist d-tubocurarine was found to block hSK1 and rSK2 with IC(50) values of 27 microM and 17 microM when measured at +80 mV. The inhibition by d-tubocurarine was voltage-dependent with increasing affinities at more hyperpolarized potentials. The GABA(A) receptor antagonist bicuculline methiodide also blocked hSK1 and rSK2 in a voltage-dependent manner with IC(50) values of 15 and 25 microM when measured at +80 mV. In conclusion, the pharmacological separation between SK channel subtypes expressed in mammalian cells is too small to support the notion that the apamin-insensitive afterhyperpolarization of neurones is mediated by hSK1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Partial apamin sensitivity of human small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2002 Nov;366(5):470-7. doi: 10.1007/s00210-002-0622-2. Epub 2002 Sep 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12382077
-
The pharmacology of hSK1 Ca2+-activated K+ channels expressed in mammalian cell lines.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Feb;129(4):627-30. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703111. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10683185 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the outer pore region of the apamin-sensitive Ca2+-activated K+ channel rSK2.Toxicon. 2004 Jun 15;43(8):951-60. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.03.025. Toxicon. 2004. PMID: 15208028
-
Small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels as targets of CNS drug development.Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004 Jun;3(3):161-7. doi: 10.2174/1568007043337472. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004. PMID: 15180477 Review.
-
Modulation of small conductance calcium-activated potassium (SK) channels: a new challenge in medicinal chemistry.Curr Med Chem. 2003 Apr;10(8):625-47. doi: 10.2174/0929867033457908. Curr Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12678783 Review.
Cited by
-
Large-Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels and Voltage-Dependent Sodium Channels in Human Cementoblasts.Front Physiol. 2021 Apr 20;12:634846. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.634846. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33959036 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of gene transcription by voltage-gated L-type calcium channel, Cav1.3.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 20;290(8):4663-4676. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.586883. Epub 2014 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25538241 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of SK2 channel from chicken short hair cells.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2005 Jun;191(6):491-503. doi: 10.1007/s00359-005-0601-4. Epub 2005 May 3. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15868189
-
Dendritic HCN2 channels constrain glutamate-driven excitability in reticular thalamic neurons.J Neurosci. 2007 Aug 8;27(32):8719-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1630-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17687049 Free PMC article.
-
Apical SK potassium channels and Ca2+-dependent anion secretion in endometrial epithelial cells.J Physiol. 2008 Feb 1;586(3):717-26. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.142877. Epub 2007 Nov 29. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18048454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ÄMMÄLÄ C., MOORHOUSE A., GRIBBLE F., ASHFIELD R., PROKS P., SMITH P.A., SAKURA H., COLES B., ASHCROFT S.J.H., ASHCROFT F.M. Promiscuous coupling between the sulphonylurea receptor and inwardly rectifying potassium channels. Nature. 1996;379:545–548. - PubMed
-
- AUGUSTE P., HUGUES M., GRAVE B., GRESQUIERE J.C., MAES P., TARTAR A., ROMEY G., SCHWEITZ H., LAZDUNSKI M. Leirotoxin I (Scyllatoxin), a peptide ligand for Ca2+-activated K+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;256:4753–4759. - PubMed
-
- BLATZ A.L., MAGLEBY K.L. Single apamin-blocked Ca-activated K+ channels of small conductance in cultured rat skeletal muscle. Nature. 1986;323:718–720. - PubMed
-
- CAMPOS-ROSA J., DUNN P.M., GALANAKIS D., GANELLIN C.R., JENKINSON D.H., YANG D. 1997. World Patent Application, WO 97/48705
-
- CAMPOS-ROSA J., GALANAKIS D., GANELLIN C.R., DUNN P.M., JENKINSON D.H. Bis-quinolinium Cyclophanes: 6,10-Diaza - 3(1,3) 8 (1,4) - dibenzena - 1,5(1,4) - diquinolinacyclodecaphane (UCL 1684), the first nanomolar, non-peptidic blocker of the apamin-sensitive Ca2+-activated K+ channel. J. Med. Chem. 1998;41:2–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

