Nitroblue tetrazolium blocks BK channels in cerebrovascular smooth muscle cell membranes
- PMID: 10696106
- PMCID: PMC1571925
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703143
Nitroblue tetrazolium blocks BK channels in cerebrovascular smooth muscle cell membranes
Abstract
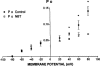
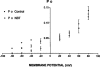
The effects of p-nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) on large conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels (BK channels) in enzymatically dispersed rat cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells (CVSMCs) were examined. Patch clamp methods were employed to record single BK channel currents from inside-out patches of CVMC membrane maintained at 21 - 23 degrees C. When applied to the cytoplasmic face of inside-out membrane patches (internally applied NBT), micromolar concentrations of NBT reversible reduced the mean open time of BK channels, without changing channel conductance. NBT altered the frequency distribution of BK channel open times from a two exponential to a single exponential form. In the absence of NBT, mean channel open time increased on membrane depolarization. In the presence of internally applied NBT, mean channel open became essentially independent of membrane potential. Internally applied NBT also reduced the mean closed time of BK channels when measured at membrane potentials in the range -80 mV to +20 mV. The combined effects of internal NBT on mean open and closed times resulted in the suppression of BK channel open probability when measured at positive membrane potentials. When applied to the external membrane face, micromolar concentrations of NBT reduced mean channel open time progressively as the membrane was hyperpolarized, and also reduced open probability at negative membrane potentials. A model is proposed in which NBT alters channel gating by binding to a site at or near to the cytoplasmic membrane face. Externally applied NBT suppressed BK channel open probability at concentrations which also inhibit nitric oxide synthase (NOS). Therefore, the potential role of potassium channel block in NBT actions previously attributed to NOS inhibition is discussed.
Figures

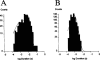



Similar articles
-
Internally applied endotoxin and the activation of BK channels in cerebral artery smooth muscle via a nitric oxide-like pathway.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Jan;123(1):5-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701570. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9484848 Free PMC article.
-
Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels of high conductance in smooth muscle cells isolated from rat cerebral arteries.J Physiol. 1993 Mar;462:529-45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019567. J Physiol. 1993. PMID: 8331591 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of nitric oxide donors, S-nitroso-L-cysteine and sodium nitroprusside, on the whole-cell and single channel currents in single myocytes of the guinea-pig proximal colon.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Feb;123(3):505-17. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701605. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9504392 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium- and voltage-gated BK channels in vascular smooth muscle.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Sep;470(9):1271-1289. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2151-y. Epub 2018 May 11. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 29748711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological roles of the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel.Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6(10):1025-30. doi: 10.2174/156802606777323764. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16787277 Review.
References
-
- ARDATI K.O., BAJAKIAN K.M., TABBARA K.S. Effect of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency on neutrophil function. Acta Haematol. 1997;97:211–215. - PubMed
-
- ARMSTEAD W.M. Superoxide generation links protein kinase C activation to impaired ATP-sensitive K+ channel function after brain injury. Stroke. 1999;30:153–159. - PubMed
-
- ASANO M., MASUZAWA-ITO K., MATSUDA T., SUZUKI Y., OYAMA H., SHIBUYA M., SUGITA K. Increased Ca2+ influx in the resting state maintains the myogenic tone and activates charybdotoxin-sensitive K+ channels in dog basilar artery. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1993;13:969–977. - PubMed
-
- BINDER R.A., JENCKS J.A., RATH C.E., CHESLEY J. Nitroblue tetrazolium reduction test in pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 1975;45:299–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

