Selective inhibition of the oxidation of ferrous iron or sulfur in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans
- PMID: 10698768
- PMCID: PMC91939
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.3.1031-1037.2000
Selective inhibition of the oxidation of ferrous iron or sulfur in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans
Abstract
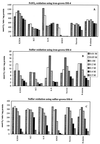
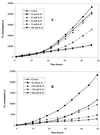
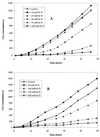
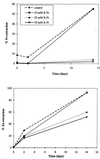
The oxidation of either ferrous iron or sulfur by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans was selectively inhibited or controlled by various anions, inhibitors, and osmotic pressure. Iron oxidation was more sensitive than sulfur oxidation to inhibition by chloride, phosphate, and nitrate at low concentrations (below 0.1 M) and also to inhibition by azide and cyanide. Sulfur oxidation was more sensitive than iron oxidation to the inhibitory effect of high osmotic pressure. These differences were evident not only between iron oxidation by iron-grown cells and sulfur oxidation by sulfur-grown cells but also between the iron and sulfur oxidation activities of the same iron-grown cells. Growth experiments with ferrous iron or sulfur as an oxidizable substrate confirmed the higher sensitivity of iron oxidation to inhibition by phosphate, chloride, azide, and cyanide. Sulfur oxidation was actually stimulated by 50 mM phosphate or chloride. Leaching of Fe and Zn from pyrite (FeS(2)) and sphalerite (ZnS) by T. ferrooxidans was differentially affected by phosphate and chloride, which inhibited the solubilization of Fe without significantly affecting the solubilization of Zn.
Figures
References
-
- Blake R C, II, Shute E A. Respiratory enzymes of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Kinetic properties of an acid-stable iron:rusticyanin oxidoreductase. Biochemistry. 1994;33:9220–9228. - PubMed
-
- Brierley C L. Bacterial leaching. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1978;6:207–219. - PubMed
-
- Corbett C M, Ingledew W J. Is Fe3+/2+ cycling an intermediate in sulfur oxidation by Fe2+-grown Thiobacillus ferrooxidans? FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1986;41:1–6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

