Transformation of Acinetobacter sp. strain BD413(pFG4DeltanptII) with transgenic plant DNA in soil microcosms and effects of kanamycin on selection of transformants
- PMID: 10698801
- PMCID: PMC91972
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.3.1237-1242.2000
Transformation of Acinetobacter sp. strain BD413(pFG4DeltanptII) with transgenic plant DNA in soil microcosms and effects of kanamycin on selection of transformants
Abstract
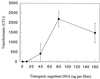
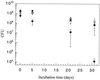
Here we show that horizontal transfer of DNA, extracted from transgenic sugar beets, to bacteria, based on homologous recombination, can occur in soil. Restoration of a 317-bp-deleted nptII gene in Acinetobacter sp. strain BD413(pFG4) cells incubated in sterile soil microcosms was detected after addition of nutrients and transgenic plant DNA encoding a functional nptII gene conferring bacterial kanamycin resistance. Selective effects of the addition of kanamycin on the population dynamics of Acinetobacter sp. cells in soil were found, and high concentrations of kanamycin reduced the CFU of Acinetobacter sp. cells from 10(9) CFU/g of soil to below detection. In contrast to a chromosomal nptII-encoded kanamycin resistance, the pFG4-generated resistance was found to be unstable over a 31-day incubation period in vitro.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transformation of Acinetobacter sp. strain BD413 by transgenic sugar beet DNA.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998 Apr;64(4):1550-4. doi: 10.1128/AEM.64.4.1550-1554.1998. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9546192 Free PMC article.
-
The natural transformation of the soil bacteria Pseudomonas stutzeri and Acinetobacter sp. by transgenic plant DNA strictly depends on homologous sequences in the recipient cells.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001 Feb 20;195(2):211-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10523.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11179654
-
Natural transformation of Acinetobacter sp. strain BD413 with cell lysates of Acinetobacter sp., Pseudomonas fluorescens, and Burkholderia cepacia in soil microcosms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Jan;66(1):206-12. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.1.206-212.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10618225 Free PMC article.
-
Human safety and genetically modified plants: a review of antibiotic resistance markers and future transformation selection technologies.J Appl Microbiol. 2005;99(1):7-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02595.x. J Appl Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15960661 Review. No abstract available.
-
Biosafety of kanamycin-resistant transgenic plants.Transgenic Res. 1992 Nov;1(6):239-49. doi: 10.1007/BF02525165. Transgenic Res. 1992. PMID: 1301215 Review.
Cited by
-
Marker rescue studies of the transfer of recombinant DNA to Streptococcus gordonii in vitro, in foods and gnotobiotic rats.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Oct;69(10):6121-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.10.6121-6127.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14532070 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmid size determines adsorption to clay and breakthrough in a saturated sand column.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 22;10(9):e29679. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29679. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38707295 Free PMC article.
-
Will transgenic plants adversely affect the environment?J Biosci. 2005 Sep;30(4):515-48. doi: 10.1007/BF02703726. J Biosci. 2005. PMID: 16184014 Review.
-
Sexual isolation in Acinetobacter baylyi is locus-specific and varies 10,000-fold over the genome.Genetics. 2009 Aug;182(4):1165-81. doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.103127. Epub 2009 May 27. Genetics. 2009. PMID: 19474200 Free PMC article.
-
Symbiotic nitrogen fixation and endophytic bacterial community structure in Bt-transgenic chickpea (Cicer arietinum L).Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 25;10(1):5453. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62199-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32214159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arumuganathan K, Earle E D. Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 1991;9:208–218.
-
- Becker J, Siegert H, Logemann J, Schell J. Biologische Sicherheit. Vol. 3. 1994. Begleitende sicherheitsforschung zur freisetzung gentechnisch veränderter petunien; pp. 563–578. Bundesministerium für Forschung und Technologie, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Broer I, Dröge-Laser W, Gerke M. Examination of the putative horizontal gene transfer from transgenic plants to agrobacteria. In: Schmidt E R, Hankeln T, editors. Transgenic organisms and biosafety, horizontal gene transfer, stability of DNA and expression of transgenes. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer Verlag; 1996. pp. 67–70.
-
- Cieslinski G, van Rees K C J, Szmigielska A M, Huang P M. Low molecular weight organic acids released from roots of durum wheat and flax into sterile nutrient solutions. J Plant Nutr. 1997;20:753–764.
-
- de Vries J, Wackernagel W. Detection of nptII (kanamycin resistance) genes in genomes of transgenic plants by marker-rescue transformation. Mol Gen Genet. 1998;257:606–613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

