Staphylococcal surface display of metal-binding polyhistidyl peptides
- PMID: 10698802
- PMCID: PMC91973
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.3.1243-1248.2000
Staphylococcal surface display of metal-binding polyhistidyl peptides
Abstract
Recombinant Staphylococcus xylosus and Staphylococcus carnosus strains were generated with surface-exposed chimeric proteins containing polyhistidyl peptides designed for binding to divalent metal ions. Surface accessibility of the chimeric surface proteins was demonstrated and the chimeric surface proteins were found to be functional in terms of metal binding, since the recombinant staphylococcal cells were shown to have gained Ni(2+)- and Cd(2+)-binding capacity, suggesting that such bacteria could find use in bioremediation of heavy metals. This is, to our knowledge, the first time that recombinant, surface-exposed metal-binding peptides have been expressed on gram-positive bacteria. Potential environmental or biosensor applications for such recombinant staphylococci as biosorbents are discussed.
Figures

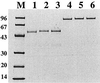

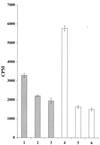
References
-
- Andréoni C, Goetsch L, Libon C, Samuelson P, Nguyen T N, Robert A, Uhlén M, Binz H, Ståhl S. Flow cytometric quantification of surface-displayed recombinant receptors on staphylococci. BioTechniques. 1997;23:696–704. - PubMed
-
- Brower J B, Ryan R L, Pazirandeh M. Comparison of ion-exchange resins and biosorbents for the removal of heavy metals from plating factor wastewater. Environ Sci Technol. 1997;31:2910–2914.
-
- Brown S. Metal-recognition by repeating polypeptides. Nat Biotechnol. 1997;15:269–272. - PubMed
-
- Demleitner G, Götz F. Evidence for importance of the Staphylococcus hyicus lipase pro-peptide in lipase secretion, stability and activity. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994;121:189–197. - PubMed
-
- Dieckmann G R, McRorie D K, Tierney D L, Utschig L M, Singer C P, O'Halloran T V, Penner-Hahn J E, DeGrado W F, Pecoraro V L. De novo design of mercury-binding two- and three-helical bundles. J Am Chem Soc. 1997;119:6195–6196.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

