TRAPP stably associates with the Golgi and is required for vesicle docking
- PMID: 10698928
- PMCID: PMC305626
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.5.862
TRAPP stably associates with the Golgi and is required for vesicle docking
Abstract
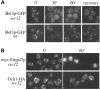
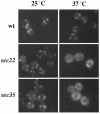
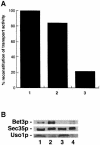
Bet3p, a component of a large novel complex called TRAPP, acts upstream of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-Golgi SNAREs. Unlike the SNAREs, which reside on multiple compartments, Bet3p is localized exclusively to Golgi membranes. While other proteins recycle from the Golgi to the ER, Bet3p and other TRAPP subunits remain associated with this membrane under conditions that block anterograde traffic. We propose that the persistent localization of TRAPP to the Golgi may be important for its role in docking vesicles to this membrane. Consistent with this proposal, we find that transport vesicles fail to bind to Golgi membranes in vitro in the absence of Bet3p. Binding is restored by the addition of cytosol containing Bet3p. These findings indicate that TRAPP stably associates with the Golgi and is required for vesicle docking.
Figures


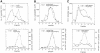
References
-
- Barlowe C. and Schekman, R. (1993) SEC12 encodes a guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor essential for transport vesicle budding from the ER. Nature, 365, 347–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

