Camel heavy-chain antibodies: diverse germline V(H)H and specific mechanisms enlarge the antigen-binding repertoire
- PMID: 10698934
- PMCID: PMC305632
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.5.921
Camel heavy-chain antibodies: diverse germline V(H)H and specific mechanisms enlarge the antigen-binding repertoire
Abstract
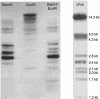
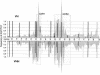
The antigen-binding site of the camel heavy-chain antibodies devoid of light chain consists of a single variable domain (V(H)H) that obviously lacks the V(H)-V(L) combinatorial diversity. To evaluate the extent of the V(H)H antigen-binding repertoire, a germline database was constructed from PCR-amplified V(H)H/V(H) segments of a single specimen of Camelus dromedarius. A total of 33 V(H)H and 39 V()H unique sequences were identified, encoded by 42 and 50 different genes, respectively. Sequence comparison indicates that the V(H)Hs evolved within the V(H) subgroup III. Nevertheless, the V(H)H germline segments are highly diverse, leading to a broad structural repertoire of the antigen-binding loops. Seven V(H)H subfamilies were recognized, of which five were confirmed to be expressed in vivo. Comparison of germline and cDNA sequences demonstrates that the rearranged V(H)Hs are extensively diversified by somatic mutation processes, leading to an additional hypervariable region and a high incidence of nucleotide insertions or deletions. These diversification processes are driven by hypermutation and recombination hotspots embedded in the V(H)H germline genes at the regions affecting the structure of the antigen-binding loops.
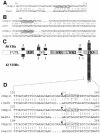
Figures


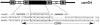
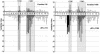
Similar articles
-
Analysis of heavy and light chain sequences of conventional camelid antibodies from Camelus dromedarius and Camelus bactrianus species.J Immunol Methods. 2014 Mar;405:35-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 18. J Immunol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24444705
-
The specific variable domain of camel heavy-chain antibodies is encoded in the germline.J Mol Biol. 1998 Jan 23;275(3):413-8. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1477. J Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9466919
-
Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains.Nature. 1993 Jun 3;363(6428):446-8. doi: 10.1038/363446a0. Nature. 1993. PMID: 8502296
-
Emergence and evolution of functional heavy-chain antibodies in Camelidae.Dev Comp Immunol. 2003 Feb;27(2):87-103. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(02)00071-x. Dev Comp Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12543123 Review.
-
Single domain antibodies: comparison of camel VH and camelised human VH domains.J Immunol Methods. 1999 Dec 10;231(1-2):25-38. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(99)00138-6. J Immunol Methods. 1999. PMID: 10648925 Review.
Cited by
-
Camelid nanobodies with high affinity for broad bean mottle virus: a possible promising tool to immunomodulate plant resistance against viruses.Plant Mol Biol. 2015 Mar;87(4-5):355-69. doi: 10.1007/s11103-015-0282-5. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Plant Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25648551
-
On the humanization of VHHs: Prospective case studies, experimental and computational characterization of structural determinants for functionality.Protein Sci. 2024 Nov;33(11):e5176. doi: 10.1002/pro.5176. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 39422475 Free PMC article.
-
High-level expression of Camelid nanobodies in Nicotiana benthamiana.Transgenic Res. 2010 Aug;19(4):575-86. doi: 10.1007/s11248-009-9338-0. Epub 2009 Oct 28. Transgenic Res. 2010. PMID: 19862637
-
A recombinant dromedary antibody fragment (VHH or nanobody) directed against human Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Oct;67(19):3371-87. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0387-6. Epub 2010 May 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20458517 Free PMC article.
-
Llama peripheral B-cell populations producing conventional and heavy chain-only IgG subtypes are phenotypically indistinguishable but immunogenetically distinct.Immunogenetics. 2019 Apr;71(4):307-320. doi: 10.1007/s00251-018-01102-9. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Immunogenetics. 2019. PMID: 30656359
References
-
- Almagro J.C., Hernandez, I., del Carmen, R. and Vargas-Madrazo, E. (1997) The differences between the structural repertoires of VH germ-line gene segments of mice and humans: implication for the molecular mechanism of the immune response. Mol. Immunol., 34, 1199–1214. - PubMed
-
- Becker R.S. and Knight, K.L. (1990) Somatic diversification of immunoglobulin heavy chain VDJ genes: evidence for somatic gene conversion in rabbits. Cell, 63, 987–997. - PubMed
-
- Berek C., Berger, A. and Apel, M. (1991) Maturation of the immune response in germinal centers. Cell, 67, 1121–1129. - PubMed
-
- Brodeur P.H. and Riblet, R. (1984) The immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (Igh-V) locus in the mouse. I. One hundred Igh-V genes comprise seven families of homologous genes. Eur. J. Immunol., 14, 922–930. - PubMed
-
- Cha R.S. and Thilly, W.G. (1993) Specificity, efficiency and fidelity of PCR. PCR Methods Appl., 3, S18–S29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

