Hormone activation induces nucleosome positioning in vivo
- PMID: 10698943
- PMCID: PMC305641
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.5.1023
Hormone activation induces nucleosome positioning in vivo
Abstract
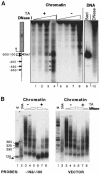
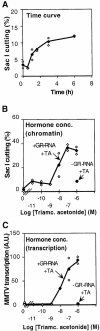
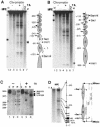
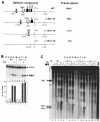
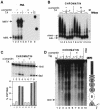
The mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) promoter is induced by glucocorticoid hormone. A robust hormone- and receptor-dependent activation could be reproduced in Xenopus laevis oocytes. The homogeneous response in this system allowed a detailed analysis of the transition in chromatin structure following hormone activation. This revealed two novel findings: hormone activation led to the establishment of specific translational positioning of nucleosomes despite the lack of significant positioning in the inactive state; and, in the active promoter, a subnucleosomal particle encompassing the glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-binding region was detected. The presence of only a single GR-binding site was sufficient for the structural transition to occur. Both basal promoter elements and ongoing transcription were dispensable. These data reveal a stepwise process in the transcriptional activation by glucocorticoid hormone.
Figures
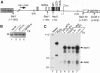
References
-
- Almouzni G. and Wolffe, A.P. (1993) Replication-coupled chromatin assembly is required for repression of basal transcription in vivo. Genes Dev., 7, 2033–2047. - PubMed
-
- Archer T.K., Lefebvre, P., Wolford, R.G. and Hager, G.L. (1992) Transcription factor loading on the MMTV promoter: a bimodal mechanism for promoter activation. Science, 255, 1573–1576. - PubMed
-
- Buetti E. and Kuhnel, B. (1986) Distinct sequence elements involved in the glucocorticoid regulation of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. J. Mol. Biol., 190, 379–389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

