Loss of FBP function arrests cellular proliferation and extinguishes c-myc expression
- PMID: 10698944
- PMCID: PMC305642
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.5.1034
Loss of FBP function arrests cellular proliferation and extinguishes c-myc expression
Abstract
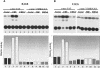
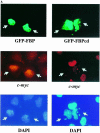
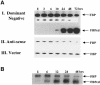
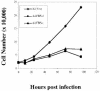
The c-myc regulatory region includes binding sites for a large set of transcription factors. The present studies demonstrate that in the absence of FBP [far upstream element (FUSE)-binding protein], which binds to the single-stranded FUSE, the remainder of the set fails to sustain endogenous c-myc expression. A dominant-negative FBP DNA-binding domain lacking effector activity or an antisense FBP RNA, expressed via replication-defective adenovirus vectors, arrested cellular proliferation and extinguished native c-myc transcription from the P1 and P2 promoters. The dominant-negative FBP initially augmented the single-stranded character of FUSE; however, once c-myc expression was abolished, melting at FUSE could no longer be supported. In contrast, with antisense FBP RNA, the single-stranded character of FUSE decreased monotonically as the transcription of endogenous c-myc declined. Because transcription is the major source of super-coiling in vivo, we propose that by binding torsionally strained DNA, FBP measures promoter activity directly. We also show that FUSE is predicted to behave as a torsion-regulated switch poised to regulate c-myc and to confer a higher order regulation on a large repertoire of factors.
Figures


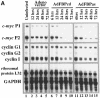


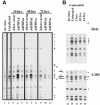

References
-
- Aghib D.F., Bishop, J.M., Ottolenghi, S., Guerrasio, A., Serra, A. and Saglio, G. (1990) A 3′ truncation of MYC caused by chromosomal translocation in a human T-cell leukemia increases mRNA stability. Oncogene, 6, 707–711. - PubMed
-
- Avigan M.I., Strober, B. and Levens, D. (1990) A far upstream element stimulates c-myc expression in undifferentiated leukemia cells. J. Biol. Chem., 265, 18538–18545. - PubMed
-
- Baber J.L., Libutti, D., Levens, D. and Tjandra, N. (1999) High precision solution structure of the C-terminal KH domain of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K, a c-myc transcription factor. J. Mol. Biol., 18, 949–962. - PubMed
-
- Bazar L., Meighen, D., Harris, V., Duncan, R., Levens, D. and Avigan, M. (1995). Targeted melting and binding of a DNA regulatory element by a transactivator of c-myc. J. Biol. Chem., 270, 8241–8248. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

